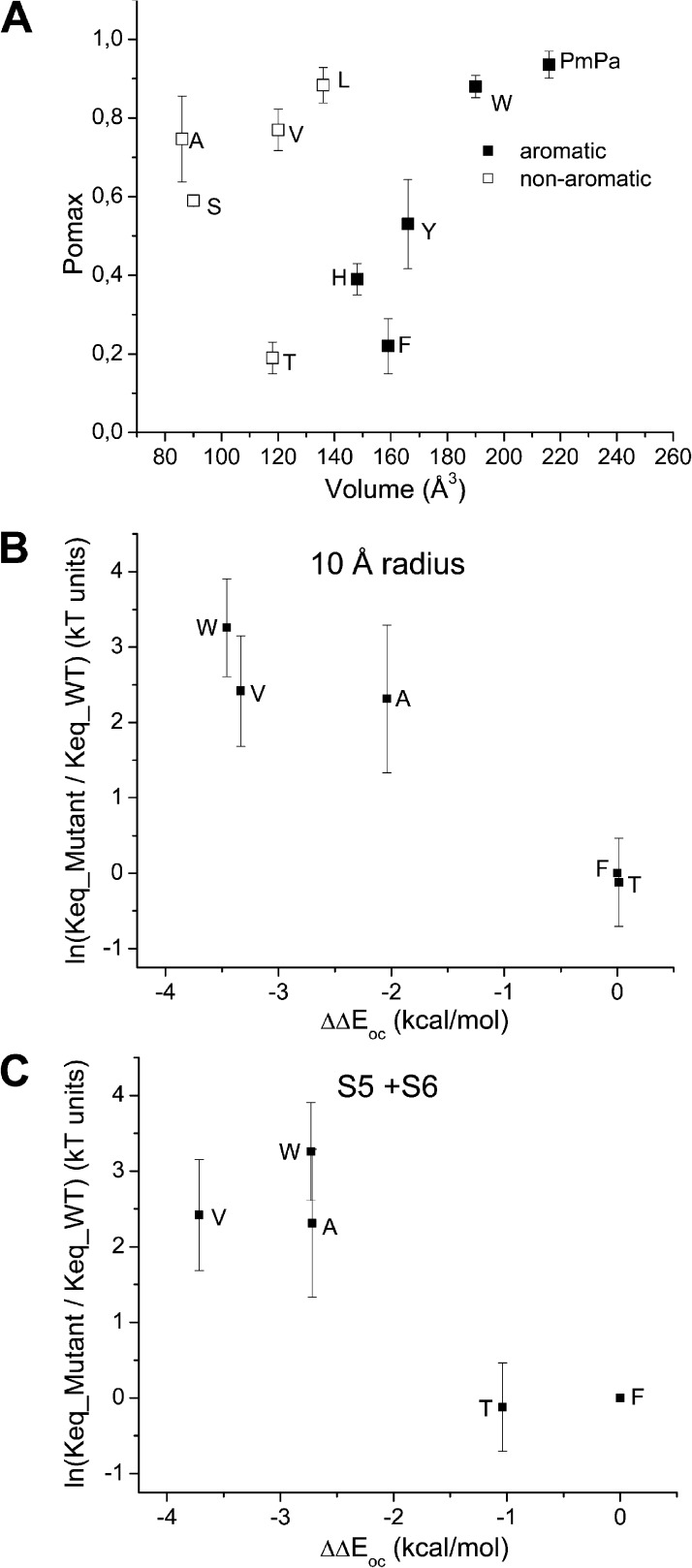
Figure 7.
(A) Effect on Pomax of substituting F248 by either nonaromatic or aromatic residues. Scatter plot of Pomax as a function of the residue volume. This analysis reveals two distinct sets of data. Whereas there was a modest but significant increase in Pomax as a function of volume size for Ala (A), Val (V), and Leu (L), drastic changes were observed with the aromatic (Phe [F], Tyr [Y], His [H], Trp [W], and pMpa) residues. Importantly, aromatic residues such as Phe (F) and Tyr (Y) showed significant lower Pomax values compared with nonaromatic amino acids of similar sizes, such as Val (V) or Leu (L), suggesting specific effects related to the presence of an aromatic residue at 248. (B and C) Ln(Keq_mutant/Keq_wild_type), where Keq = Pomax/(1 − Pomax) plotted as a function of the energy perturbation ΔΔEoc coming from mutating residue 248 for the F248T, F248V, F248A, and F248W mutants. ΔΔEoc was calculated as ΔEoc_mutant − ΔEoc_wild_type, where ΔEoc is the difference in nonbonded energy for residue 248 between the open and closed state. Nonbonded energies were computed from >32–64-ns MD trajectories by averaging the van der Waals plus electrostatic interactions between the residue at 248 and the surrounding atoms within a 10-Å radius (excluding lipids and water) (B), or between the residue at 248 and the S5 and S6 helices (C). The resulting analysis is in agreement with the Pomax ranking F248T ≈ F248 < F248A ≈ F248V < F248W observed experimentally, while establishing an energy equivalence (ΔΔEoc ≈ 0) between a Thr (T) and a Phe (F) at 248. The latter result argues for π–π interactions involving F248 and the S5 transmembrane segment in the closed state as being determinant in setting Pomax for the KCa3.1 wild-type channel. These simulations also predict an increase in Pomax relative to wild type with the F248W mutant despite the possibility of π–π interactions with S5, an effect attributable to the mutation F248W stabilizing to a greater extent the channel open than closed configurations. In contrast, the Pomax increase seen with the F248A and F248V mutants appeared to be related to a stronger destabilization for the channel closed than open state.