Figure 1. Role of mutant BRAF in preventing apoptosis in melanoma cells.
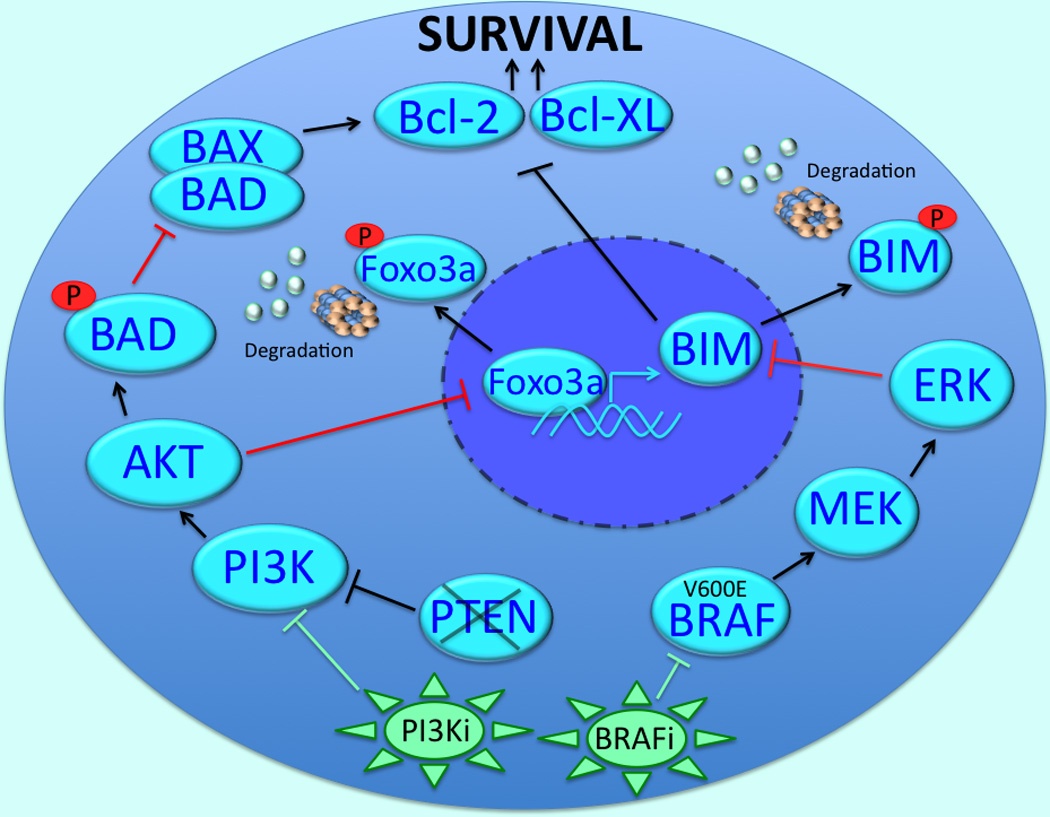
The inhibition of BRAF decreases the phosphorylation of BIM through the MEK/ERK pathway, preventing its proteasomal degradation. Once stabilized, BIM antagonizes the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL and leads to apoptosis induction. In PTEN-null melanoma cells, BRAF inhibition leads to the increased PI3K/AKT-mediated phosphorylation of FOXO3a resulting in reduced BIM transcription. Inhibition of BRAF in PTEN null melanoma cells also impairs apoptosis through the AKT-mediated phosphorylation and inactivation of BAD. The phosphorylation of BAD prevents its binding to Bax and relieves the antagonism of Bax on Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL. Intrinsic BRAF inhibitor resistance in the PTEN-null cells can be overcome through dual inhibition of BRAF and PI3K.
