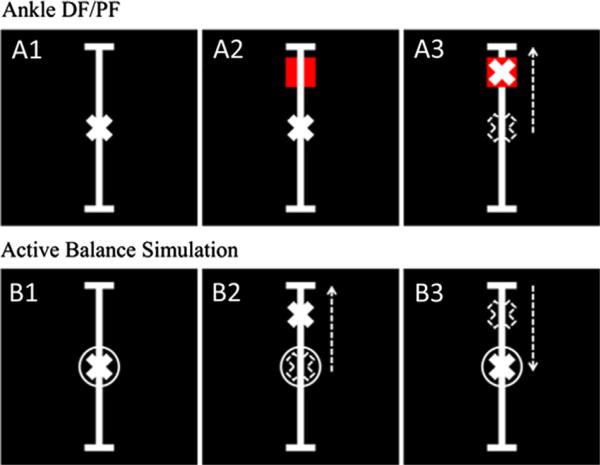
Fig. 2.
The visual stimulation control was defined as panel A1. The A2 and A3 panels describe the ankle DF/PF task in which subjects were asked to do a simple ankle dorsiflexion (DF) or plantarflexion (PF) to move a cross hair into a red square. The B panels describe the active balance simulation task in which the cross hair represented a summation of an unpredictable sum of sines perturbation with a frequency similar to that of human postural plus the center of pressure of the subject. The subjects were instructed to counteract the sum of sines perturbation using ankle DF/PF and keep the cross hair in the circle.