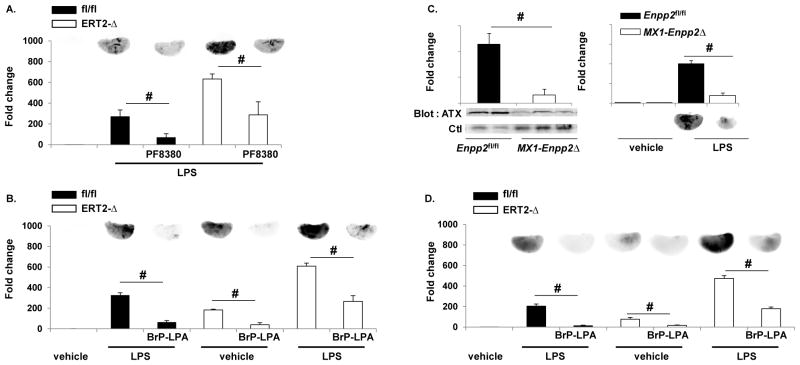
Figure 6. Attenuating LPA production or signaling promotes endothelial barrier function.
The autotaxin inhibitor PF8380 (1mg/kg) (A) or the LPA receptor pan-antagonist (5mg/kg) BrP-LPA (B) were administered 30 minutes prior to LPS, and protein leak in Ppap2bfl/fl (fl/fl) or ERT2-Ppap2bΔ (ERT2-Δ) lungs (n = 3/group/genotype) was measured with EBD as described. Both PF8380 and BrP-LPA reduced EBD accumulation in lung. # P<0.05 by ANOVA. (C) To verify that autotaxin was involved in LPS-mediated permeability, mice with reduced plasma autotaxin were generated using the Mx1-Cre transgene that is activated by administration of pI-pC. Plasma autotaxin (ATX) levels were lower in Mx1-Enpp2Δ mice (left) as was EBD accumulation in lungs after LPS (right). # P<0.05 by t-test. (D) The LPA receptor pan-antagonist BrP-LPA was administered to ventilated/perfused lungs prior to infusion of LPS via the pulmonary artery and protected from protein leak Ppap2bfl/fl (fl/fl) or ERT2-Ppap2bΔ (ERT2-Δ) lungs. # P<0.05 by ANOVA.