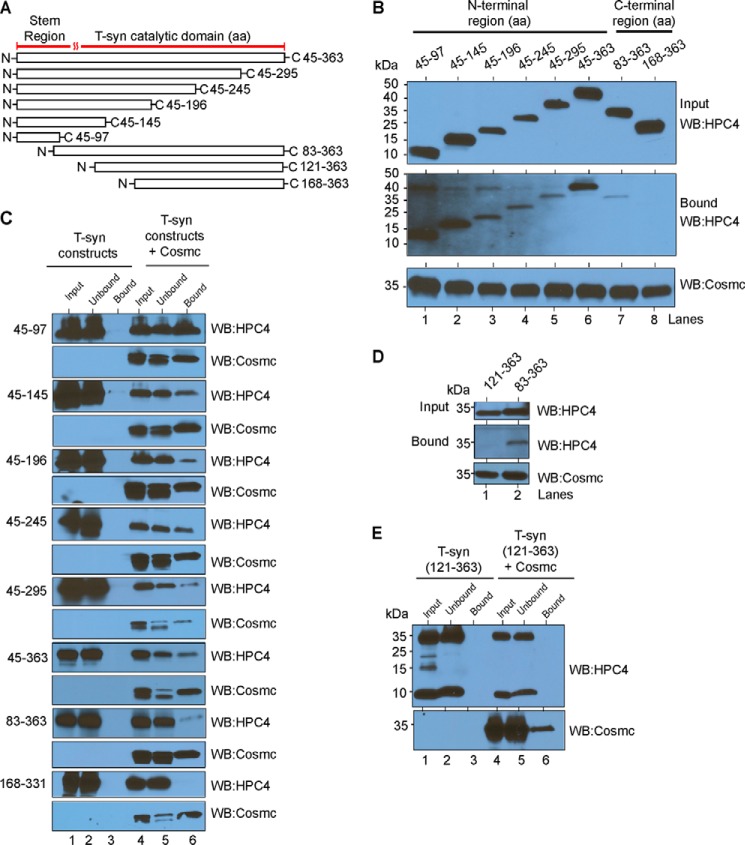
FIGURE 1.
Identification and functional characterization of a novel Cosmc binding region in human T-synthase, the CBRT. A, schematics depicting the truncated soluble versions of HPC4-T-synthase. All constructs contain a signal sequence and HPC4 tag followed by different lengths of lumenal T-synthase as indicated. B and C, cosmc binds to the N-terminal stem region of T-synthase. B, input and bound fractions from the pulldown experiment were immunoblotted using monoclonal antibody against HPC4 for T-synthase, and the His-sCosmc used for pulldown was detected by monoclonal antibody against Cosmc. C, whole cell lysates from Hi-5 cells expressing various constructs of the human N-terminal HPC4 epitope-tagged soluble T-synthase (HPC4-sT-syn) expressed individually or co-expressed with human N-terminal His-tagged soluble Cosmc (His-sCosmc) were incubated with Ni-NTA beads followed by pulldown experiments. Input, unbound, and bound fractions were detected by antibody against HPC4 for T-synthase (top panels). Similarly, the amount of Cosmc used in the pulldown experiment was detected by antibody against Cosmc (bottom panels). D, pulldown experiment demonstrating that aa 83-121 in the N-terminal stem region of T-synthase are essential for binding to Cosmc. Input, bound, and amount of Cosmc used in the pulldown experiment were analyzed as described in B. E, pulldown experiment showing HPC4-sT-syn 121-363 does not bind to Cosmc or beads alone. A representative example of two independent experiments is shown. The data in B and D were repeated at least two independent times, and a representative example is shown. WB, Western blot.