FIGURE 4.
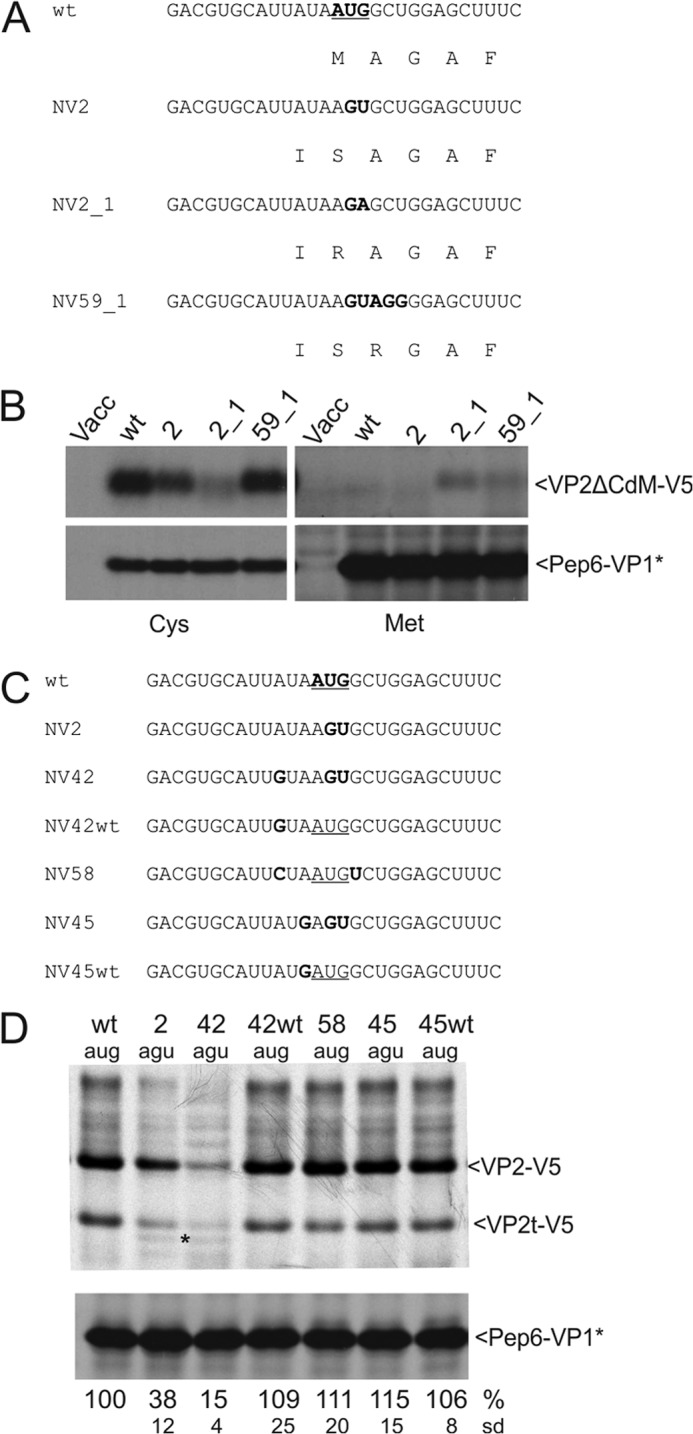
Importance of start site sequence and location for initiation position and efficiency. A, sequences represent part of the TURBS. Top, wild type sequence is shown with the VP2 start codon given in boldface. Below the nucleotide sequence, the deduced VP2 amino acid sequence starting with the Met encoded by the original start site is given. Below the WT sequences, the equivalent information is given for the tested mutants. For constructs with mutated VP2 start codon, the amino acid encoded by the altered codon plus the residue upstream thereof is given. The AUG in WT as well as the residues altered in the mutants are highlighted in boldface. B, gels with the proteins precipitated with antiserum anti-V5 (upper part) or anti-pep6 (lower part) after transient expression of the indicated constructs. All constructs are shown twice, either after labeling with [35S]Cys (left part) or [35S]Met (right part). Please note that in the constructs expressed here, all internal Met codons were replaced by Cys codons and that the VP2 coding ORF contains a deletion of the C-terminal codons 107–268. The designation VP2ΔCdM reflects the truncation (ΔC) and absence of internal Met codons (dM). Vacc, vaccinia virus. C, sequences represent part of the TURBS. Top, wild type sequence is shown with the VP2 start codon given in boldface. Below, mutants with substitutions affecting the start codon or the codon upstream thereof are shown with the changes highlighted in boldface. Please note that in constructs NV45 and NV45WT, the VP1 stop codon was changed from UAA to UGA. D, gel with the proteins precipitated after transient expression (antisera as described for Fig. 3). Numbers indicating the transfected constructs and the sequences present at the position of the original start site are given above the gel. As described in legend to Fig. 3, the calculated VP2 expression efficiencies in percent and the standard deviations (sd) are given below the autoradiographs (relative to pNVWT, normalized to the expression level of Pep6-VP1*). For VP2t-V5, see legend Fig. 2.
