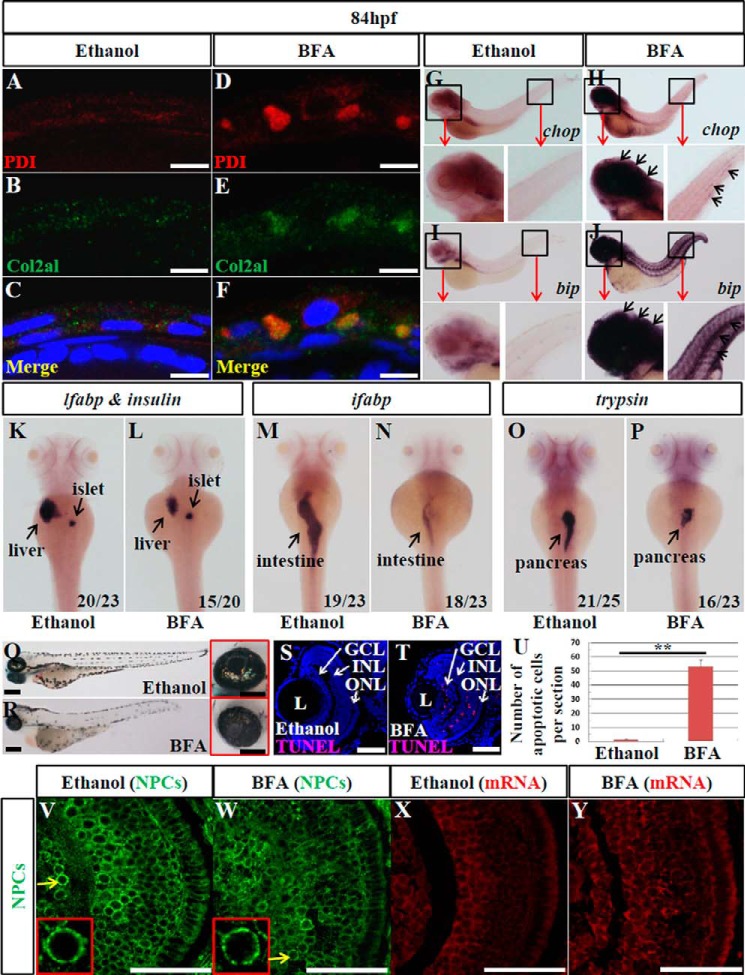
FIGURE 5.
BFA treatment destroys the COPII function and impedes digestive organ development. A–F, double immunostaining of PDI (ER marker) and collagen II (Col2a1, secretory protein) in ethanol-treated (A–C) and BFA-treated (D–F) embryos at 84 hpf. A and D, immunostaining of PDI (shown in red). B and E, immunostaining of Col2a1 (in green). C and F, merge of PDI and Col2a1 staining. G–J, WISH analysis of chop and bip in ethanol-treated (G and I) and BFA-treated (H and J) embryos at 84 hpf. K–P, WISH analysis using lfabp (for the liver) plus insulin (for the endocrine pancreas) (K and L), ifabp (for the intestine) (M and N), and trypsin (for the exocrine pancreas) (O and P) probes for the analysis of digestive organs in ethanol-treated (K, M, and O) and BFA-treated (L, N, and P) embryos at 84 hpf. In each case, the number of total embryos examined (as denominator) and the number of embryos exhibiting the displayed phenotype (as numerator) are shown on the bottom right. Q and R, bright field images of ethanol-treated (Q) and BFA-treated (R) embryos at 84 hpf. Higher magnification of the eye image is shown on the right correspondingly. S–U, representative image of TUNEL analysis of apoptosis in ethanol-treated (S) and BFA-treated (T) retina at 84 hpf. U, average number of apoptotic cells in these samples were shown (n = 3, four sections from each embryo were used for counting the apoptotic cells). V and W, immunostaining of nuclear pores in ethanol-treated (V) and BFA-treated (W) embryos at 84 hpf. X and Y, mRNA export assay in ethanol-treated (X) and BFA-treated (Y) retinas at 84 hpf. L, lens. Scale bar, 10 μm (A–F), 300 μm (Q and R), 150 μm (inset in Q and R), and 50 μm (S, T, and V–Y). **, p < 0.01.