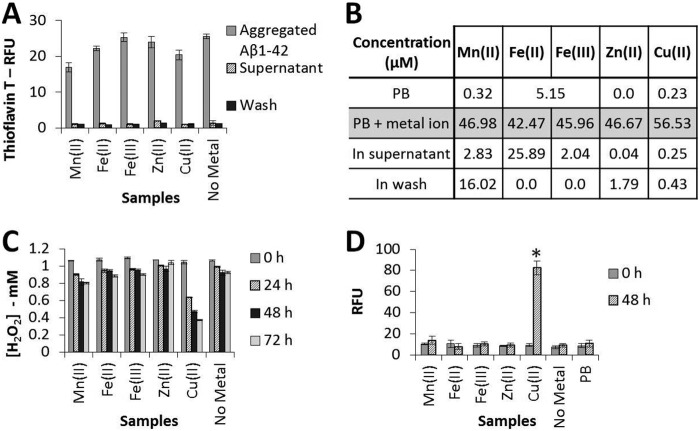
FIGURE 2.
Aggregates formed by incubation of Aβ(1–42) in the presence of Cu(II) ions degrade H2O2 and contain carbonyl groups. Aβ(1–42) (50 μm) was incubated in 10 mm PB at 37 °C for 144 h in the presence or absence of an equimolar concentration of a range of different metal ions, as indicated, prior to centrifugation for 1 h in a Beckman airfuge. The supernatant was removed for analysis, and the pellet containing aggregated Aβ was resuspended in 10 mm PB and then centrifuged for a further 1 h before removal of the second supernatant (Wash). The final pellet was resuspended in 1 mm H2O2 to an Aβ concentration of 25 μm. This final suspension was incubated at 37 °C for up to 72 h and assayed for H2O2 concentration every 24 h and for carbonyl group formation at 0 and 48 h. A, ThT fluorescence data (mean ± S.D., n = 3) for the Aβ samples prior to pelleting, the first supernatant, and the subsequent wash. RFU, relative fluorescence unit. B, metal ion concentrations (average of two independent inductively coupled plasma MS analyses) for the Aβ samples prior to pelleting, the first supernatant and subsequent wash. C, Amplex red data (mean ± S.D., n = 3) for the final suspension incubated with H2O2. D, carbonyl group formation data (mean ± S.D., n = 4) for the final suspension incubated with H2O2. *, p ≤ 0.001; Tukey's HSD.