Figure 8.
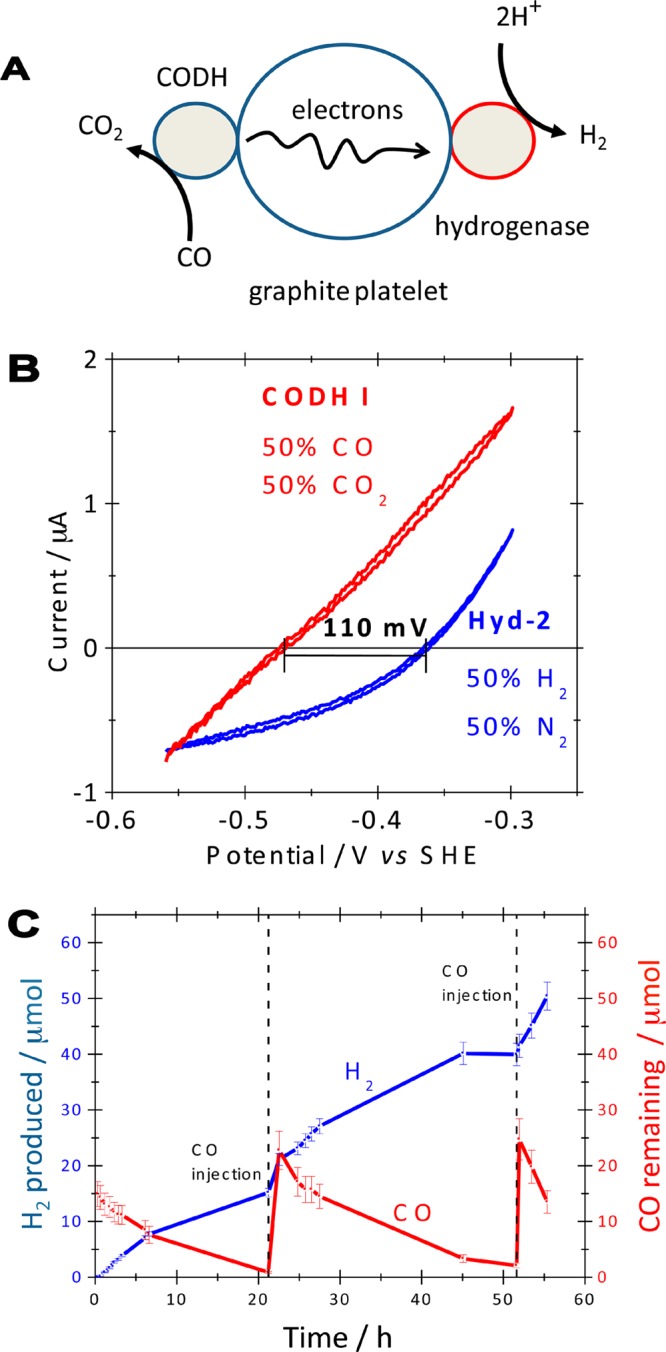
(A) Cartoon representation of an enzymatic device for catalysis of the water–gas shift reaction. Electrons released by CODH-catalyzed CO oxidation are transferred through a graphite particle to a CO-tolerant hydrogenase that reduces protons to H2. (B) Typical cyclic voltammograms (from separate experiments) showing the reversibility of electrocatalysis by CODHCh I and a hydrogenase (Hyd-2) from E. coli, measured at pH 6.0, 30 °C, scan rate 10 mV s–1, electrode rotation rate 2500 rpm. (C) H2 production and CO depletion over the course of 55 h at pH 6.0, 30 °C, as quantified by GC analysis. Fresh aliquots of CO were introduced at the times indicated. Adapted with permission from ref (51). Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society.
