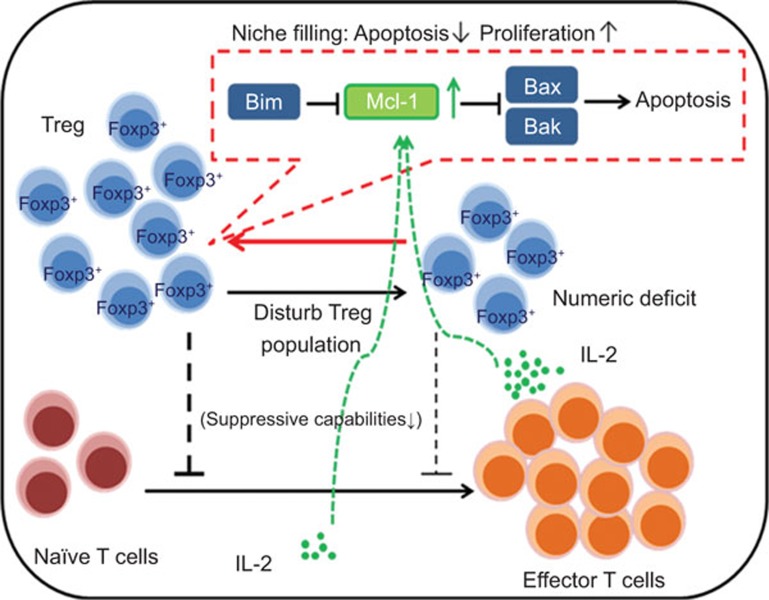
Figure 1.
A proposed regulatory mechanism of Treg homeostasis and survival. In the steady state, the interactions between pro-apoptotic Bim, anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 and apoptotic regulators Bax and Bak actively maintain the homeostatic population of Tregs. When the homeostatic population of Tregs is disturbed, signals provided by IL-2 and costimulatory signals upregulate anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 expression, which in turn inhibits the Bak and Bax-mediated intrinsic apoptosis pathway and subsequently allows Tregs to proliferate during the niche-filling process. Treg, regulatory T cell.