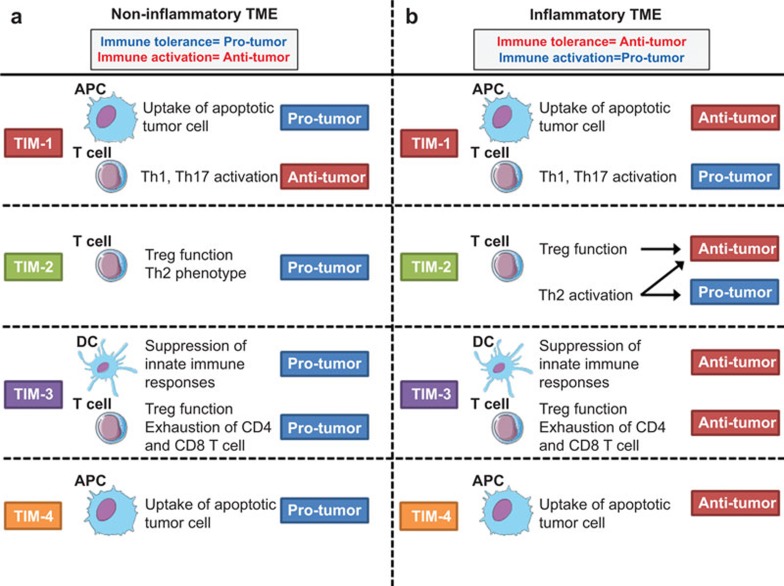
Figure 3.
The dual role of TIM family members in sterile or inflammatory tumor microenvironments. TIM members may serve as dual regulators of antitumor immune responses depending on the quality of the tumor microenvironment. (a) In sterile, non-inflammatory TMEs, TIM-1 and TIM-4 on APCs suppress antigen-specific immune responses by facilitating tolerogenic phagocytosis. Moreover, TIM-2 may create tolerogenic environments by activating Treg populations, whereas TIM-3 negatively regulates DAMP-mediated innate immune signals and compromises tumor-specific CTL responses. (b) In contrast, immunoregulatory activities mediated by TIM-3 and TIM-4 may have a beneficial role in preventing protumorigenic inflammation, while TIM-1 and TIM-2 have dual roles in tumorigenesis by regulating T helper cell differentiation. DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; TIM, T-cell immunoglobulin mucin; Treg, regulatory T cell.