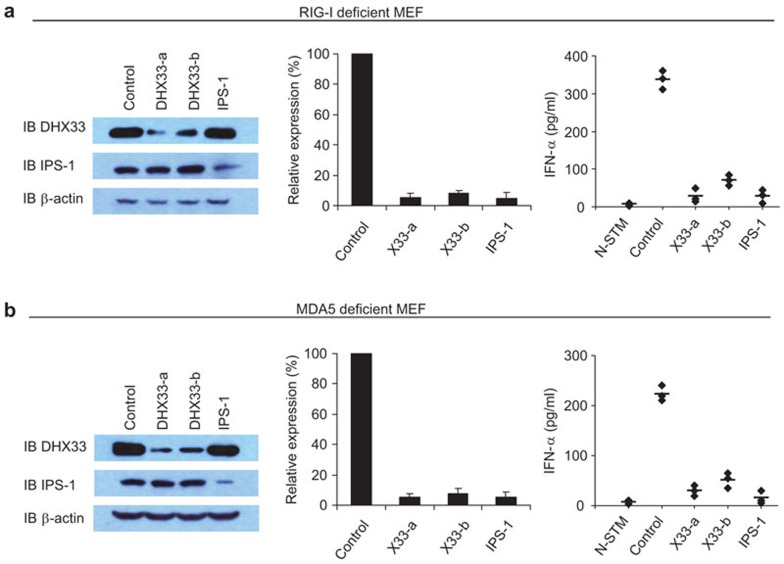
Figure 4.
DHX33 signaling is independent of MDA5 and RIG-I signaling. (a) IB showing the knockdown efficiency of shRNAs targeting the indicated proteins in RIG-I-deficient MEFs (left panel). QPCR showing the knockdown efficiency of shRNAs targeting the indicated genes in RIG-I-deficient MEFs (middle panel). Scrambled shRNA served as a control. ELISA of IFN-α production by RIG-I-deficient MEFs treated with the indicated shRNAs after 16 h of stimulation with 5 µg/ml short poly I:C delivered to the cells by Lipofectamine 2000 (right panel). (b) IB showing the knockdown efficiency of shRNAs targeting the indicated proteins in MDA5-deficient MEFs (left panel). QPCR analysis showing the knockdown efficiency of shRNAs targeting the indicated genes in MDA5-deficient MEFs (middle panel). Scrambled shRNA served as a control. ELISA of IFN-α production by MDA5-deficient MEFs treated with the indicated shRNAs after 16 h of stimulation with 2.5 µg/ml long poly I:C delivered to the cells by Lipofectamine 2000 (right panel). N-STM, unstimulated RIG-1- or MDA5-deficient MEFs treated with scrambled shRNA. The data represent the mean±s.d. of triplicate or quadruplicate measurements. Individual diamonds represent the values from each independent experiment. Bars represent the average values from at least three independent experiments. IB, immunoblot; IFN, interferon; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; QPCR, quantitative PCR; shRNA, small heteroduplex RNA.