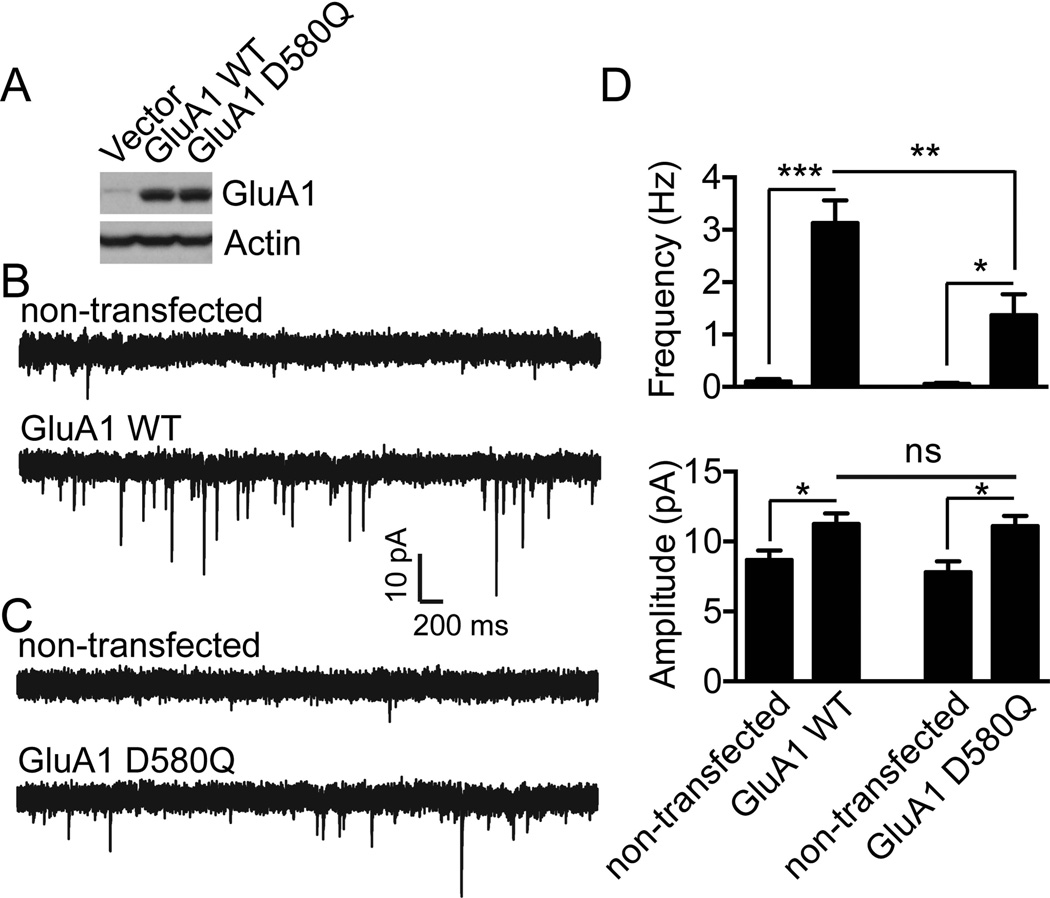
Figure 6. Disruption of GluA1 phosphorylation by CK2 impairs GluA1 synaptic targeting.
A) Lysates from HEK293T cells expressing Flag-GluA1 WT or D580Q constructs in pIRES2-EGFP vector were prepared and immunoblotted with specific antibodies as indicated. Typical result is shown. B–C) Dissociated hippocampal cultures from GluA1 knockout mice were transfected with GluA1 WT (B) or with CK2 phospho-deficient mutant (GluA1 D580Q) (C). Whole-cell voltage clamp recordings to measure miniature EPSCs (mEPSCs) were performed after transfection. As shown in (D), although both GluA1 WT and GluA1 D580Q expression enhanced mEPSC frequency and amplitude, mEPSC frequency in neurons transfected with GluA1 WT was significantly higher than that in neurons transfected with GluA1 D580Q (for GluA1 WT, n = 9 for non-transfected and GluA1 WT transfected neurons; for GluA1 D580Q, n = 6 for non-transfected control and n = 10 for GluA1 D580Q). Error bars represent S.E.M. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001.