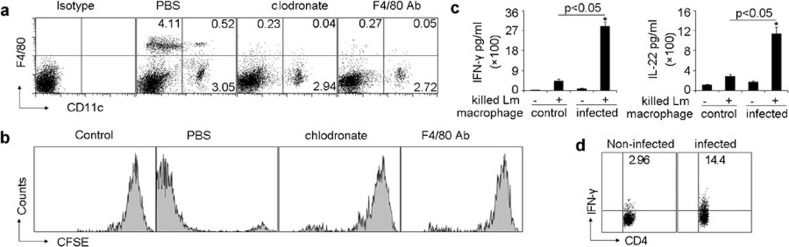
Figure 1.
Macrophages are required in DC-elicited anti-Lm T-cell responses. (a) BALB/c mice were i.p. injected with clodrolip or anti-F4/80 depleting mAb for macrophage depletion. Forty-eight hours later, splenic cells were stained with FITC-conjugated CD11c and PE-conjugated F4/80 mAbs or their isotypes and analyzed by flow cytometry. This result was the representative from four mice in each group. (b) BALB/c nude mice (n=6) with or without macrophage depletion were adoptively transferred with CFSE-labeled T cells isolated from the spleens of Lm-infected mice or naive mice (control), and 1.0×103 viable Lm were injected into these mice after 6 h. Sixty hours later, the proliferation of adoptively transferred T cells in the spleen was determined by flow cytometry. (c, d) Thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages from C57BL/6 mice (n=6) were infected with Lm for 2 h in culture dish and the cells (5×106) were then adoptively transferred to gentamycin-treated C57BL/6 mice. Seven days later, mice were killed and splenic cells were restimulated with heat-killed Lm for 24 h. The supernatants were harvested and assayed for IFN-γ and IL-22 by ELISA (c). The cells were stained and IFN-γ expression in CD4+ T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry (d). DC, dendritic cell; IFN, interferon; i.p., intraperitoneally; Lm, Listeria monocytogenes; mAb, monoclonal antibody; PE, phycoerythrin.