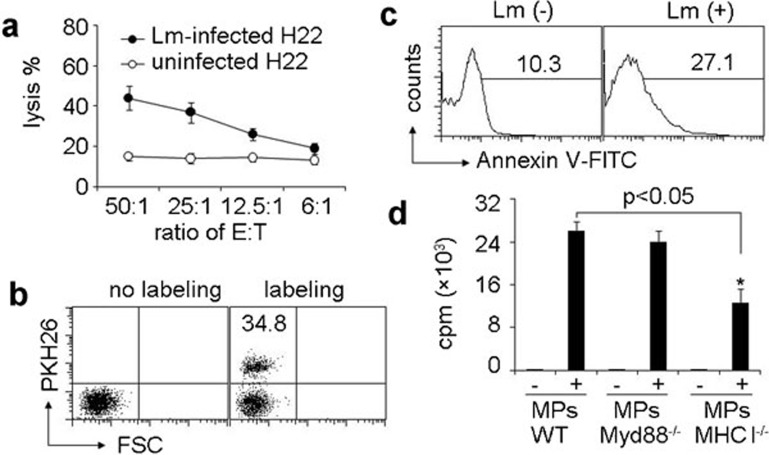
Figure 4.
DCs take up the MPs derived from macrophages and present Lm antigenicity to T cells. (a) Lm components within MPs possessed antigenicity. MPs were isolated from the supernatants of macrophages with or without Lm infection. T cells isolated from Lm-infected mouse spleen were cocultured with MP-treated DCs for 10 days and acted as effector cells. CFSE-labeled H22 cells with or without Lm infection were used as target cells. The cytolysis assay was performed with various ratios of effector to target cells. The lysis was analyzed with flow cytometry. (b) DCs took up MPs. Macrophages were infected with Lm. The isolated MPs were stained with or without PKH26 and incubated with DCs for 6 h. The red fluorescence was determined by flow cytometry. (c) The apoptosis marker phosphatidylserine was present on the surface of MPs derived from Lm-infected macrophages. Macrophages were infected with Lm. The isolated MPs were stained with FITC-Annexin V and analyzed by flow cytometry. (d) Bone marrow-derived DCs were incubated with MPs from Lm-infected macrophages of WT, MHC-I−/− or MyD88−/− mice, respectively. Four hours later, followed by the addition of CD8+ T cells, Lm-infected mouse spleen and [3H]-thymidine incorporation was determined after 48 h of culture. *P<0.05, compared with macrophage-absent groups. CFSE, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; DC, dendritic cell; Lm, Listeria monocytogenes; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MP, microparticle; WT, wild-type.