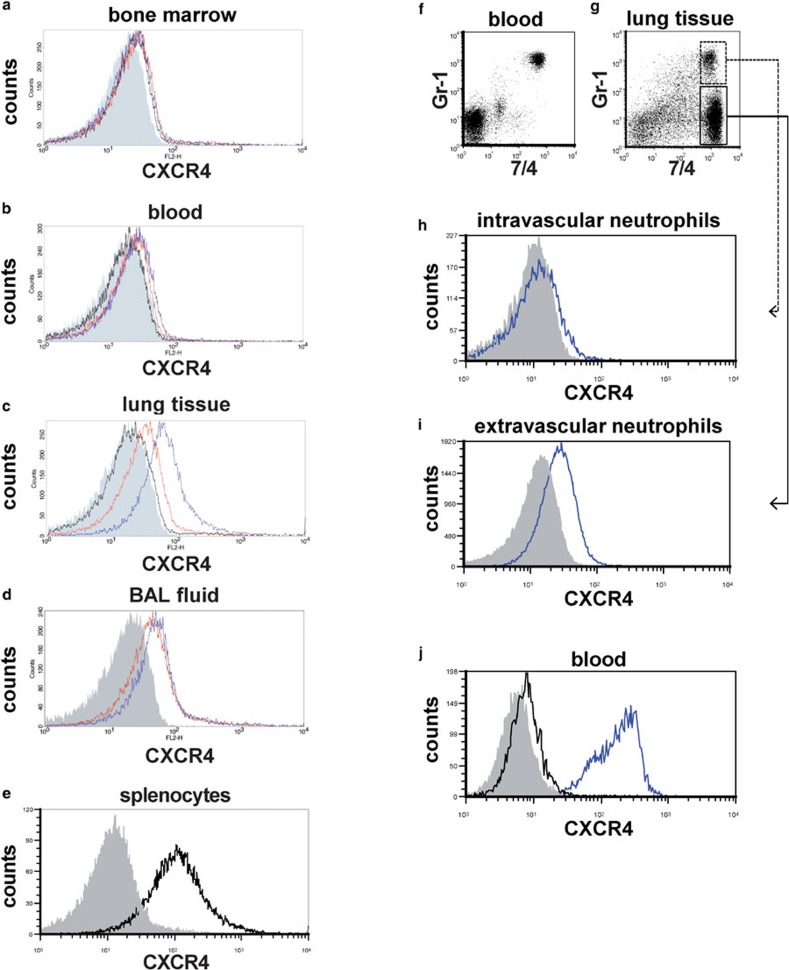
Figure 1.
Surface CXCR4 expression increased in extravascular neutrophils in the mouse lungs during LPS-induced lung injury. (a–e) Flow cytometric analyses were performed to determine the surface CXCR4 expression levels of neutrophils isolated from bone marrow (a), peripheral blood (b), lung tissue (c) and BAL fluid (d). Neutrophils were analyzed before LPS administration (black line) and at 6 h (red line) and 24 h (blue line) afterward. The filled images show the staining using an isotype-matched control antibody. We were unable to analyze the surface CXCR4 expression levels of neutrophils isolated from BAL fluid before LPS administration because there were an insufficient number of neutrophils in these samples. Splenocytes from untreated control mice were used as a positive control for CXCR4 staining (e). (f–i) The surface CXCR4 expression levels of intravascular neutrophils (g; GR-1+7/4+) and extravascular neutrophils (g; GR-1−7/4+) in the lungs at 24 h during LPS-induced lung injury were examined. Note almost all circulating neutrophils (7/4+ cells) in blood were stained with Gr-1 5 min after antibody injection (f). The blue lines show the surface CXCR4 expression levels of intravascular neutrophils (h) or extravascular neutrophils (i). The filled images show the staining using an isotype-matched control antibody. (h) The levels of intracellular CXCR4 (blue line) in neutrophils isolated from mouse blood were analyzed by staining with permeabilization. The filled image shows the staining using an isotype-matched control antibody. The black line shows the surface CXCR4 expression levels. Representative histograms or dot plots from one of three experiments that showed similar results are presented. BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.