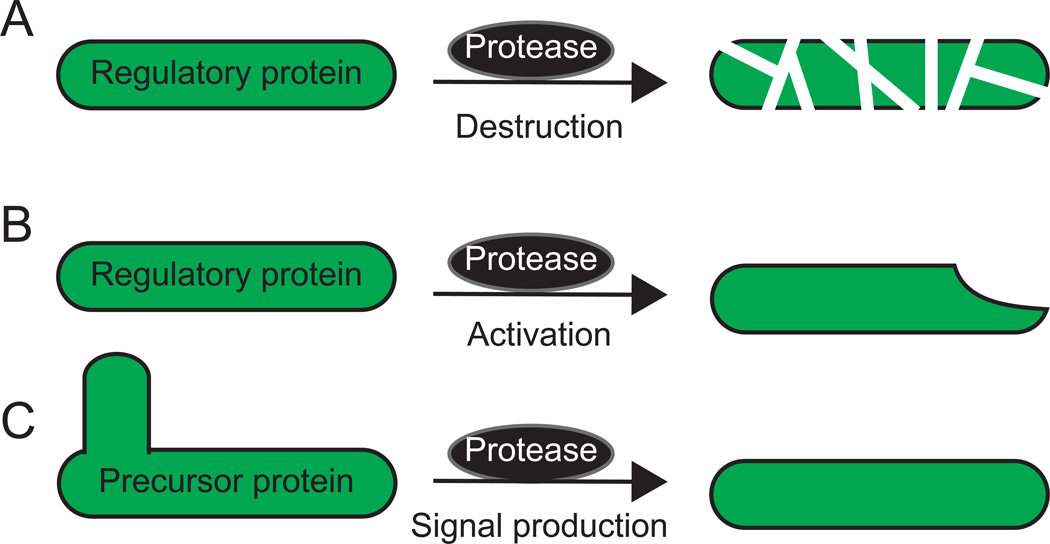
Figure 1. Events controlled by regulated proteolysis during bacterial development.
(A) Destruction of a regulatory protein by a protease, e.g., a Clp protease that processively degrades a regulatory protein.
(B) Activation of a regulatory protein by a protease, e.g., a protease (often dedicated to one specific substrate) that non-processively cleaves an inactive proprotein to produce the active regulatory protein.
(C) Production of an intercellular signal by a protease. In many cases, the protease(s) remains to be identified. A precursor protein is cleaved one or more times to produce a protein, peptide, or amino acid that acts as an intercellular signal.