Figure 1.
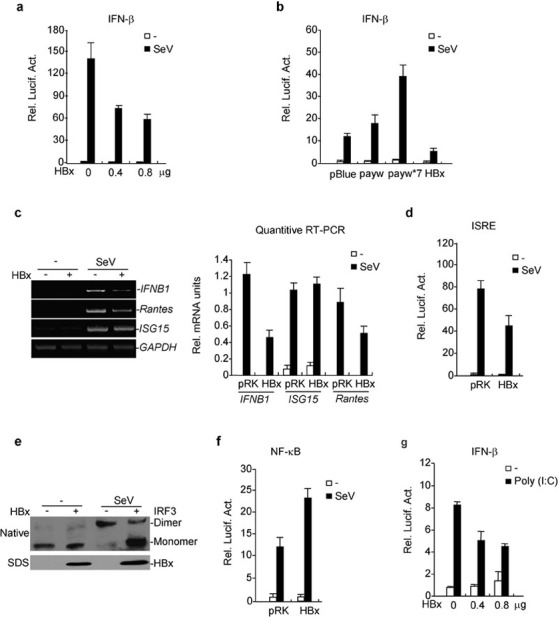
HBx inhibits virus-triggered IRF3 activation and IFN-β induction. (a) HBx inhibits SeV-induced activation of the IFN-β promoter in a dose-dependent manner. The 293 cells (1×105) were transfected with the IFN-β promoter reporter plasmid (0.1 µg) and the indicated amount of expression plasmid for HBx. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were left uninfected or infected with SeV for 12 h before luciferase assays were performed. (b) Effects of HBV and mutant replicons on SeV-triggered activation of the IFN-β promoter. Experiments were performed as in (a). (c) HBx inhibits transcription of IFNB1 and RANTES genes. The 293 cells (1×105) were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h. RT-PCR was performed 10 h after SeV infection. The quantitative software Quantity One was used to examine the amount of DNA in agarose gels; the IFN-B1, Rantes and ISG15 values were then normalized to GAPDH values. The specific values are used for graphic display. (d) HBx inhibits SeV-induced ISRE activation. The experiments were performed as in (a). (e) HBx inhibits SeV-induced dimerization of endogenous IRF3. The 293 cells (2×105) were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were infected with SeV or left uninfected for 6 h. Cell lysates were separated by native (upper panel) or SDS (bottom two panels) PAGE and analyzed with the indicated antibodies. (f) HBx does not inhibit SeV-induced NF-κB activation. The experiments were performed as in (a). (g) HBx inhibits poly(I:C)-induced activation of the IFN-β promoter. The 293 cells (1×105) were transfected with the IFN-β reporter and HBx expression plasmids. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were transfected with poly(I:C) (0.5 µg/well) or left untransfected for 12 h before luciferase assays were performed. payw: a plasmid carrying a greater-than-length (129%) HBV genome (subtype ayw); payw*7: an HBx-deficient version of the same plasmid of payw. HBV, hepatitis B virus; HBx, HBV-encoded X protein; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappaB; IFN, interferon; ISRE, IFN-stimulated response element; IRF, IFN-regulatory factor; PAGE, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; SeV, Sendai virus.
