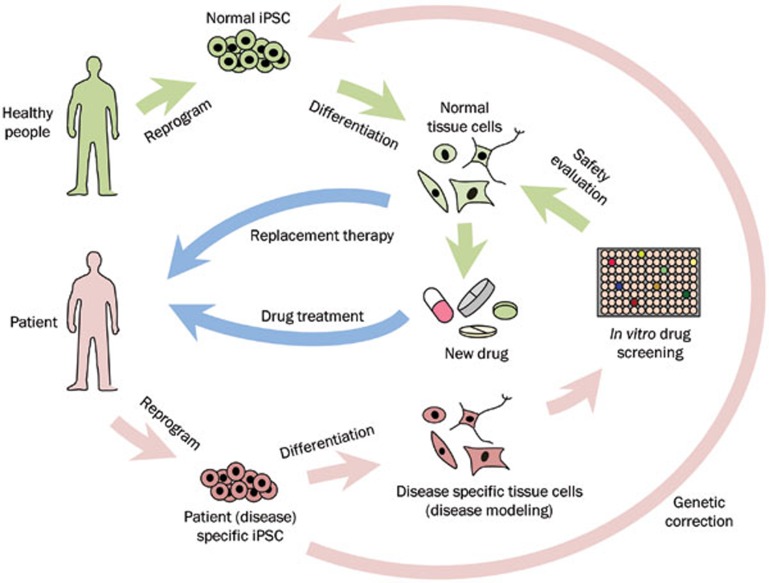
Figure 1.
The use of human iPSCs in replacement therapy, disease modeling and drug development. iPSCs from healthy people can be differentiated into various normal tissue cells, which can be transferred into patients to replace the damaged cells or tissues or used for the safety evaluation of new drugs. iPSCs carrying disease-linked mutations can be derived from patients. These patient-specific iPSCs can be genetically corrected in vitro and used for autologous cell replacement therapy, or the iPSCs can be differentiated into tissue cells harboring the disease phenotype. These cells can be used to study the mechanisms of the disease and to screen new drug.