Figure 2.
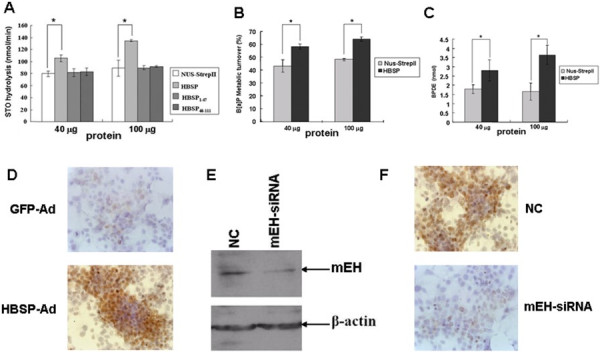
Effects of HBSP on the hydrolysis activity of mEH. (A) Effects of HBSP on the hydrolysis of STO. STO was analyzed by HPLC and quantified. The experiments were performed for three times (* P < 0.05). (B-C) Effects of HBSP on the metabolism of B[alpha]P. B[alpha]P and BPDE were analyzed by HPLC and quantified. The B[alpha]P overall metabolic turnover was expressed as% initial substrate concentration. The experiments were performed for three times. (* P < 0.05). (D-F) Effects of HBSP on the mEH-dependent BPDE-DNA adduct formation in Huh-7 hepatoma cells. After GFP-Ad or HBSP-Ad infected Huh-7 hepatoma cells were treated with B[alpha]P, cells were submitted for immunocytochemistry assay using anti-BPDE-DNA. Images were taken at × 400 magnification (D) After treating with mEH-siRNA and exposed to B[alpha]P, expression level of mEH in Huh-7 hepatoma cells were evaluated by western blot (E) and intracellualr BPDE-DNA level was detected by Immunocytochemistry assay. Images were taken at × 400 magnification (F).
