Figure 2.
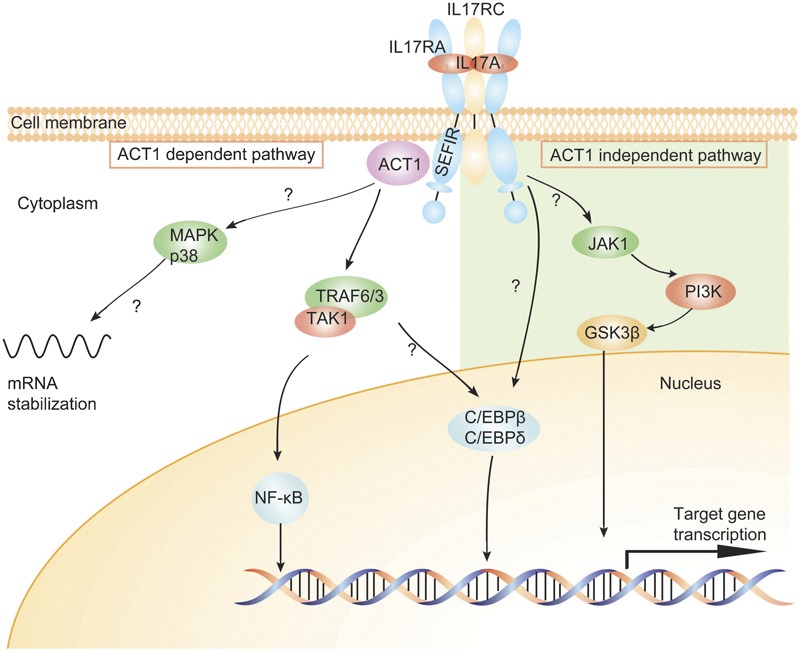
Signal pathways of IL-17. The IL-17R complex is composed of two IL-17RA and one IL-17RC; both subunits encode SEFIR domains. After activation, the intracellular IL-17 signaling includes ACT1-dependent and -independent downstream pathways. Left: the ACT1-dependent pathway: IL-17RA engages its SEFIR domain to recruit the adaptor protein ACT1. ACT1 contains a TRAF6-binding motif and can bind TRAF6, TRAF3 and TAK1, which subsequently leads to activation of the canonical NF-κB pathway. ACT1 is also required for the activation of MAPK p38, and this pathway leads to the stabilization of mRNAs, particularly those encoding chemokines and cytokines. Right: the ACT1-independent pathway involves JAK1 and PI3K, followed by subsequent inactivation of GSK-3β. Both ACT1-dependent and -independent pathways contribute to the activation of transcription factors C/EBP-β and C/EBP-δ. ACT1, nuclear factor-κB activator 1; C/EBP, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β JAK1, Janus kinase 1; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; SEFIR, SEF/IL-17R; TAK1, TGF-β-activated kinase 1; TRAF6, tumor-necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6.
