Figure 5.
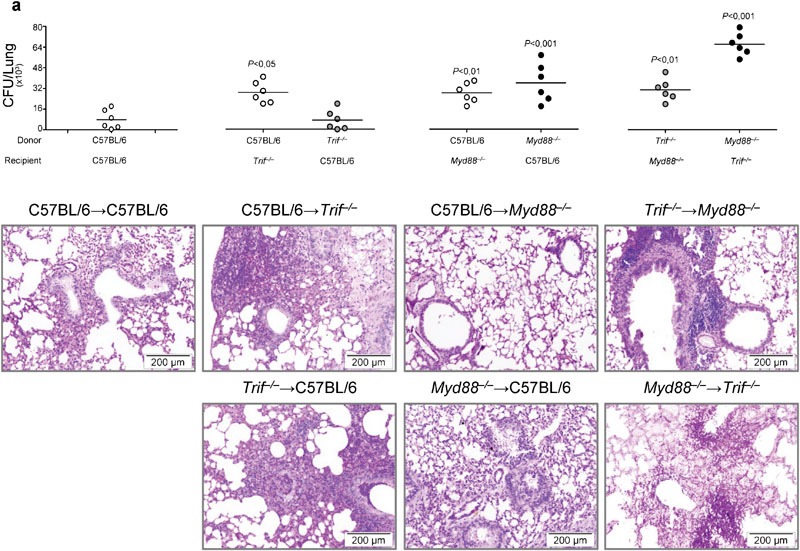
Bone marrow chimeric mice with Trif−/− non-hematopoietic cells are highly susceptible to Aspergillus fumigatus infection and inflammation. Mice were infected i.n. with live Aspergillus conidia. (a) Fungal growth (CFU±SE) and lung histology (PAS staining) in bone marrow chimeric WT and KO mice, at 3 dpi. Donor WT and KO mice received 1×106 viable bone marrow cells, 4 weeks before the infection. Note the increased susceptibility to aspergillosis, in terms of both fungal growth and the inflammatory response in the lung of chimeric mice with TRIF unresponsive non-hematopoietic cells as opposed to MyD88 unresponsive cells. Bars indicated magnifications. Data are representative of one experiment out of three. P, KO→WT, WT→KO, KO→KO versus WT→WT mice. CFU, colony-forming unit; dpi, days post-infection; i.n., intranasally; KO, knockout; PAS, periodic acid-Schiff; TRIF, Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor-inducing interferon; WT, wild-type.
