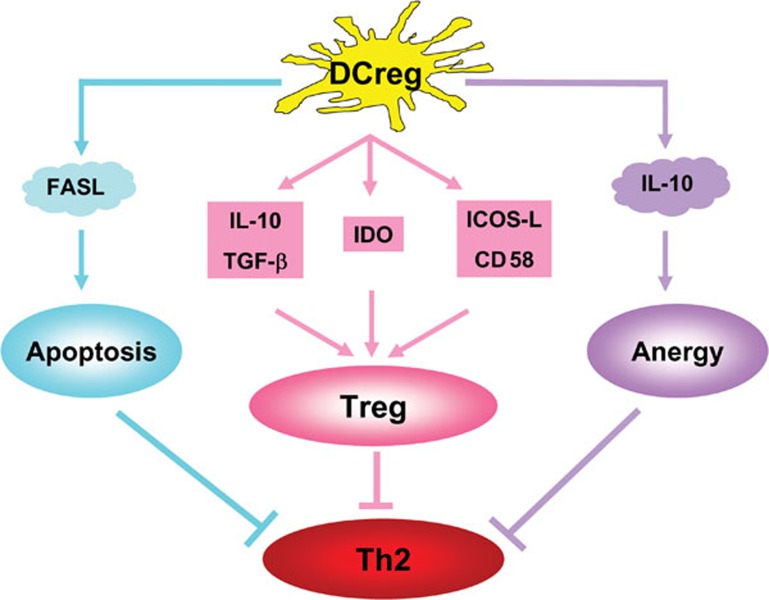
Figure 1.
The mechanisms by which tolerogenic DCs/DCregs inhibit allergic Th2 responses. DCregs induced by infection or exposure to bacterial components can inhibit allergic Th2 responses through three mechanisms: (i) DCregs can express FasL, which leads to Th2 cell apoptosis through FasL–Fas interaction (blue line); (ii) DCregs can induce allergen-specific and allergen-non-specific Tregs through the production of immunoregulatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β, enzymes such as IDO, and costimulatory surface markers (red line); and (iii) DCregs may induce Th2 cell anergy through the production of IL-10 and other cytokines. →: promoting effect; ⊣: inhibitory effect. DCreg, regulatory dendritic cell; FasL, Fas ligand; ICOS-L, inducible costimulatory ligand; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; TGF, transforming growth factor; Treg, regulatory T cell.