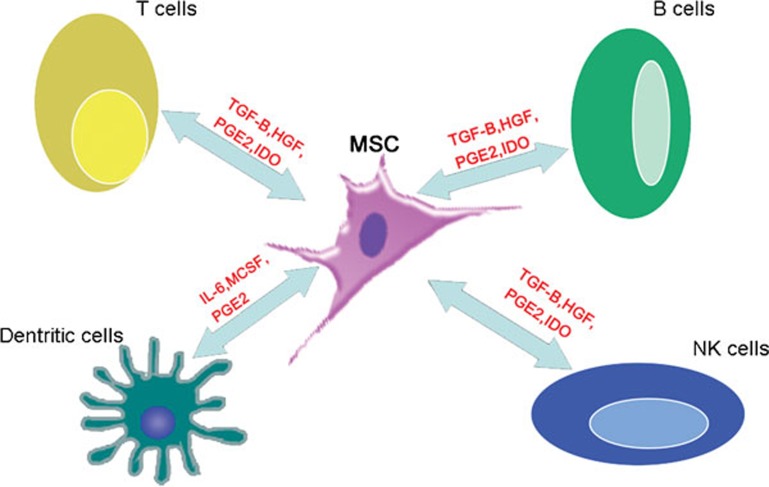
Figure 2.
Immunomodulatory properties of MSCs. MSCs modulate the functions of the immune system by interacting with a wide range of immune cells, including T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, natural killer cells and dendritic cells, by secreting dissoluble cytokines and by direct cell–cell contacts. MSCs inhibit T-cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner: the greater the number of MSCs, the greater the inhibition of T-cell proliferation. In contrast, the greater the number of MSCs, the lower the inhibition of B-cell proliferation. HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IL-6, interleukin-6; MCSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β.