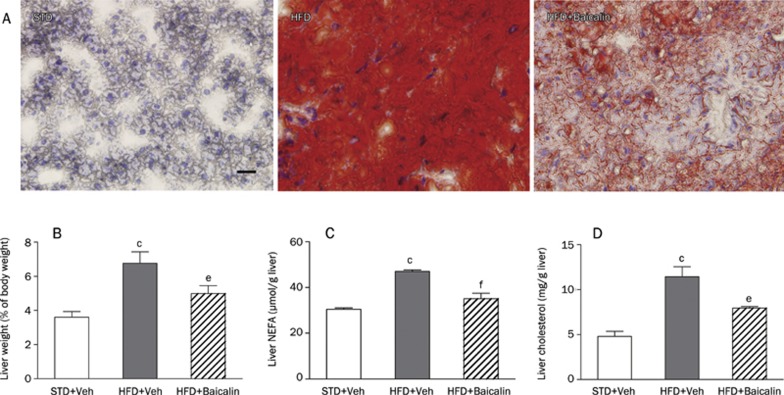
Figure 2.
Long-term baicalin administration attenuates fat accumulation in the livers of rats fed a high-fat diet (HFD). Sprague-Dawley rats were fed a standard diet and treated with vehicle (STD+Veh), fed a HFD and treated with vehicle (HFD+Veh), or fed a HFD and treated with baicalin (HFD+baicalin) at a dose of 80 mg/kg ip daily for 16 weeks. (A) Hepatic histology of a representative rat from each treatment group. Liver sections were fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin, and stained with Oil Red O and hematoxylin (original magnification, ×400). (B) Liver-to-body weight ratio of STD+Veh (open bars), HFD+Veh (solid bars), and HFD+baicalin (hatched bars). The concentrations of liver total cholesterol (C) and nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA, D) were measured as described under Materials and Methods. Scale bars indicate 200 μm. Values are given as means±SEM (n=6–8 rats per group). cP<0.01 vs STD+Veh; eP<0.05, fP<0.01 vs HFD+Veh.