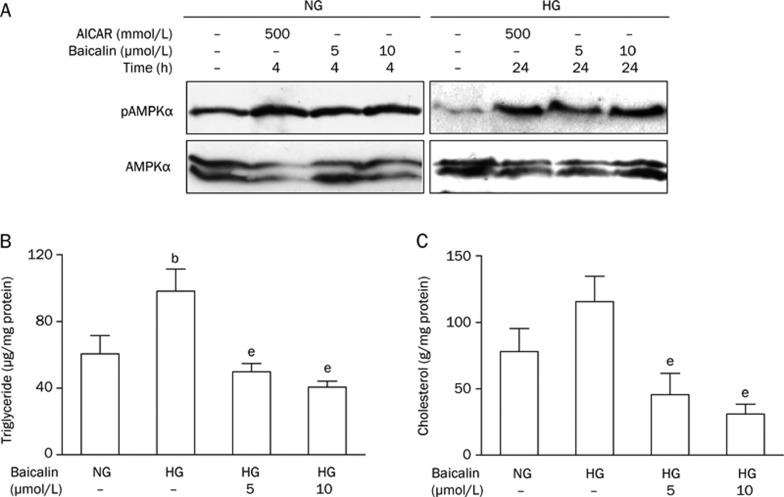
Figure 5.
Baicalin stimulates the phosphorylation of AMPK and decreases the lipid accumulation caused by high glucose concentration in HepG2 cells. (A) Representative immunoblots showing the effects of baicalin on the activation of AMPK. HepG2 cells were grown in 100-mm culture dishes until confluence. Cells were maintained in serum-free MEM medium overnight and treated with baicalin (5 and 10 μmol/L) in MEM containing either normal glucose (5.5 mmol/L, NG) or high glucose (30 mmol/L, HG) for the indicated times. AMPKα phosphorylation (pAMPK) and total AMPKα were detected by western blot analysis as described under “Materials and Methods.” AICAR was used as a positive control. Immunoblots are representative of three individual experiments. (B) and (C) Baicalin reduced the increase in lipid accumulation induced by HG in HepG2 cells. Cells were cultured in serum-free MEM overnight and incubated in MEM containing HG in the absence or presence of baicalin (5 and 10 μmol/L) for an additional 24 h. Cells in MEM containing NG in the absence of baicalin was used as the control. The data are presented as the means ± SEM of at least five experiments. bP<0.05 vs normal glucose control; eP<0.05 vs high-glucose untreated control.