Table 1. Angiogenesis inhibitors discovered in the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica since 2001.
| No | Inhibitors | Chemical structure | Origin | Targets | Antiangiogenic mechanisms | Refs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial natural products | |||||||
| 1 | Pseudolaric acid B |  |
The root bark of Pseudolarix amabilis, a TCM | Microtubulin | 1. To increase the phosphorylated c-Jun while reducing the non-phosphorylated c-Jun at Ser63/73, which impairs its function in stabilizing HIF-1α 2. To reduce HIF-1α protein by promoting its proteasome-mediated degradation; 3. To abrogate hypoxia-induced VEGF secretion via reducing HIF-1α protein. | 16,18,22,23 | |
| 2 | Triptolide | 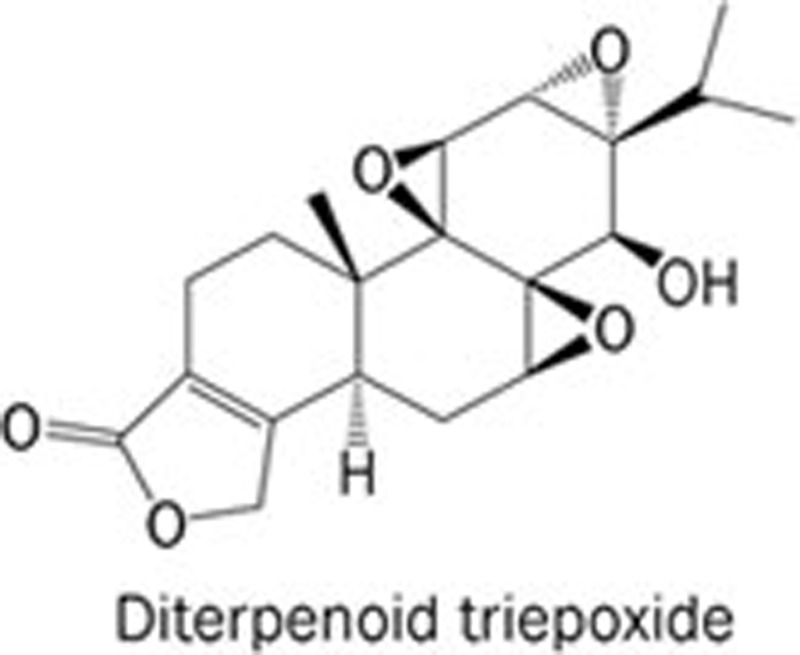 |
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F, a TCM | XPB; RNAP II | 1. To increase the levels of HIF-1α mRNA, but to reduce its transcriptional function; 2. To decrease mRNA levels of HIF-1α target genes including VEGF, BNIP3, and CAIX; 3. To lower the secretion of VEGF protein, and to reduce sprout outgrowth. | 20,21 | |
| 3 | MFTZ-1 |  |
An endophyte Streptomyces sp. ls9131 of Magnolia hookeri | Topoisomerase II | 1. To reduce HIF-1α accumulation, irrelevant to its topoisomerase II inhibition; 2. To abrogate the HIF-1α-driven increase in VEGF mRNA; 3. To reduce constitutive, HIF-1α-independent VEGF secretion and concurrently antagonize inducible, HIF-1α-dependent VEGF secretion. | 17,25 | |
| 4 | 10-Hydroxycamptothecin |  |
Camptotheca acuminata, a TCM | Topoisomerase I | 1. To inhibit proliferation, migration and tube formation of HMEC cells; 2. To inhibit angiogenesis in CAM assays; 3. To elicit apoptosis in HMEC cells. | 19 | |
| 5 | 11,11′-dideoxyverticillin |  |
The fungus Shiraia bambusicola, a TCM | VEGF VEGFR | 1. To antagonize the antiapoptotic effects of VEGF, and to inhibit VEGF-induced HUVEC migration and tube formation; 2. To completely block VEGF-induced microvessel sprouting and vessel growth; 3. To decrease VEGF secretion and to suppress VEGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of Flt-1 and KDR/Flk-1. | 6 | |
| 6 | Shiraiachrome A | 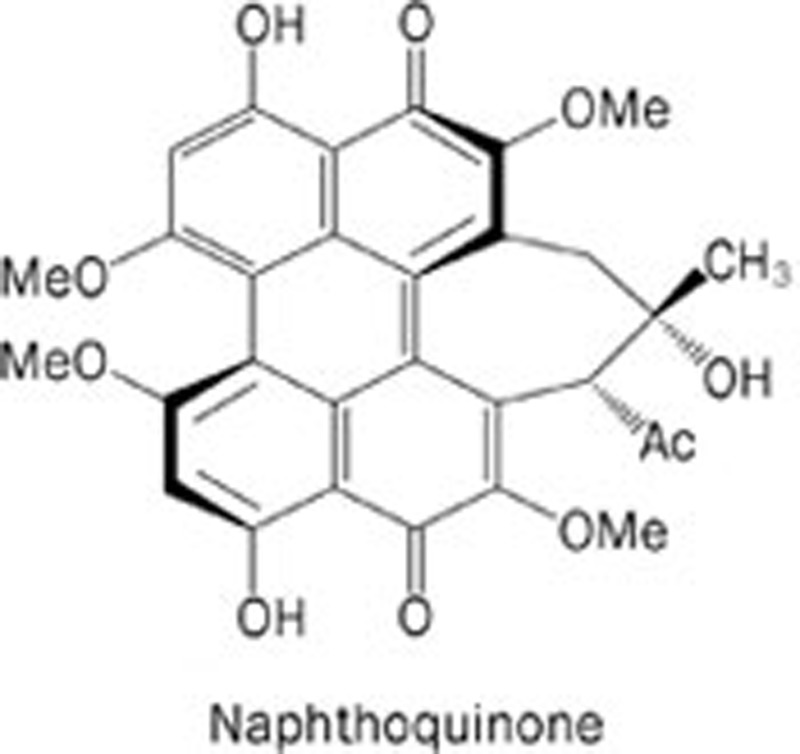 |
The fungus Shiraia bambusicola, a TCM | VEGFR-2; FGFR; PDGFR; EGFR | 1. To suppress the autophosphorylation of VEGFR-2, FGFR, PDGFR, and EGFR; 2. To inhibit the proliferation, migration, and tube formation of HMEC; 3. To inhibit the formation of new microvessels in a rat aorta culture model as well as in the CAM assay. | 7 | |
| 7 | Quercetin |  |
Many fruits and vegetables, as well as olive oil, red wine, and tea | MMP-2 | 1. To inhibit proliferation, migration, and tube formation of HMEC and HUVEC; 2. To display an antiangiogenic effect in vivo; 3. To decrease the expression and activity of MMP-2. | 29 | |
| Marine-derived natural products | |||||||
| 8 | JG3 |  |
Marine oligomannurarate blocks | Heparanase | 1. To combat heparanase activity via binding to the KKDC and QPLK domains of the heparanase molecule; 2. To abolish heparanase-driven invasion, and to inhibit the release of heparan sulfate–sequestered bFGF from the extracellular matrix, and to repress subsequent angiogenesis; 3. To inactivate bFGF-induced bFGFR and ERK1/2 phosphorylation and to block bFGF-triggered angiogenic events by binding to bFGF. | 27,42 | |
| 9 | MDOS |  |
Marine oligomannurarate blocks | HER2; EGFR; VEGFR; PDGFR; c-Kit; FGFR1; c-Src | 1. To directly inhibit HER2, EGFR, VEGFR, PDGFR, c-Kit, FGFR1 and c-Src, with little impact on FGFR2; 2. To inhibit phosphorylation of PTKs, exemplified by HER2, EGFR and VEGFR2, and downstream molecules of Erk1/2 and AKT; 3. To act as an ATP competitive inhibitor via directly binding to the residues of entrance rather than those of the ATP-binding pocket. | 8 | |
| 10 | Grateloupia longifolia polysaccharide | Sulphated polysaccharide (MW: 1.8×106) | The marine alga G longifolia | Tissue factor | 1. To decrease tissue factor at both mRNA and protein levels; 2. To inhibit proliferation of HMECs and HUVEC and tube formation and to reduce the number of migratory cells in a VEGF-independent manner; 3. To reduce new vessel formation and the vessel density in Matrigel plugs implanted in mice. | 30 | |
| 11 | Philinopside E |  |
Sea cucumber (pentacta quadrangularis) | KDR | 1. To inhibit KDR phosphorylation and downstream signaling; 2. To specifically interact with KDR extracellular domain, and to block its interaction with VEGF and the downstream signaling; 3. To markedly suppresses αvβ3 integrin-driven downstream signaling and as a result, to disturb the physical interaction between KDR and αvβ3 integrin in HMECs, followed by disruption of the actin cytoskeleton organization and decreased cell adhesion to vitronectin. | 9 | |
| 12 | Philinopside A |  |
Sea cucumber (pentacta quadrangularis) | VEGFR; FGFR1; PDGFRβ EGFR | 1. To inhibit the proliferation, migration and tube formation of HMECs; 2. To suppress the formation of new microvessels in cultured rat aorta and angiogenesis in CAM assays; 3. To inhibit VEGFR, FGFR1, PDGFRβ, and EGFR. | 10 | |
| Synthetic inhibitors | |||||||
| 13 | AL3810 |  |
Synthetic | VEGFR1; VEGFR2; FGFR1; PDGFRβ | 1. To inhibit VEGFR1, VEGFR2, FGFR1 and PDGFRβ 2. To inhibit the autophosphorylation of VEGFR2, PDGFRβ, and FGFR1 in endothelial cells; 3. To exhibit potent antiangiogenesis activity, manifested by significant inhibition of microvessel outgrowth of rat arterial ring and CAM in ex vivo angiogenesis models. | 11,31 | |
| 14 | BB |  |
Synthetic | EGFR | 1. To selectively inhibit EGFR; 2. To abrogate autophosphorylation of the EGF-stimulated EGFR and phosphorylation of its key downstream signaling molecules ERK and AKT in A549 cells; 3. To exhibit antiangiogenesis activity, as evidenced by antagonizing EGFinduced HMECS migration in vitro, blocking HMECS tube formation, and inhibiting microvessel sprouting from rat aortic rings. | 12 | |
| 15 | TKI-28 |  |
Synthetic | ErbB-2; EGFR; KDR; PDGFRβ c-kit; c-Src | 1. To inhibit ErbB-2, EGFR, KDR, PDGFRβ, c-kit and c-Src in cell-free systems; 2. To block their autophosphorylation and subsequently to downregulate phosphorylation of many downstream signaling proteins at the cellular level; 3. To inhibit cell proliferation driven by EGF, VEGF and PDGF, and cell migration and tube formation in HMECs. | 13 | |
| 16 | TKI-31 |  |
Synthetic | VEGFR2; PDGFRβ c-kit; c-Src | 1. To inhibit VEGFR2, PDGFRβ, c-kit and c-Src, showing no activity against VEGFR1 and EGFR; 2. To repress VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 in endothelial cells and PDGFBB-induced phosphorylation in fibroblast cells, leading to the inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR, MAPK42/44 (ERK) and paxillin; 3. To suppress VEGF-induced endothelial cells proliferation, migration and their differentiation into capillarylike tube formation. | 14 | |
| 17 | C9 |  |
Synthetic | Microtubulin | 1. To inhibit proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cells, and angiogenesis in aortic ring and CAM assays; 2. To induce disassembly of microtubules in endothelial cells and to downregulate Raf-MEK-ERK signaling activated by pro-angiogenic factors; 3. To disrupt capillary-like networks and newly formed vessels in vitro and to rapidly decrease perfusion of neovasculature in vivo, and to induce endothelial cell contraction and membrane blebbing in neovasculature dependent on the Rho/Rho kinase pathway. | 24 | |
Abbreviations: BNIP3, BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3; CAIX, carbonic anhydrase IX; CAM, chick chorioallantoic membrane; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular signal regulated kinase; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; FGFR1, FGF receptor 1; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha; HMEC, human dermal microvasculature endothelial cells; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; KDR, receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; MMP-2, matrix metalloproteinase-2; PDGFBB, platelet derived growth factor BB; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine.
