Figure 2.
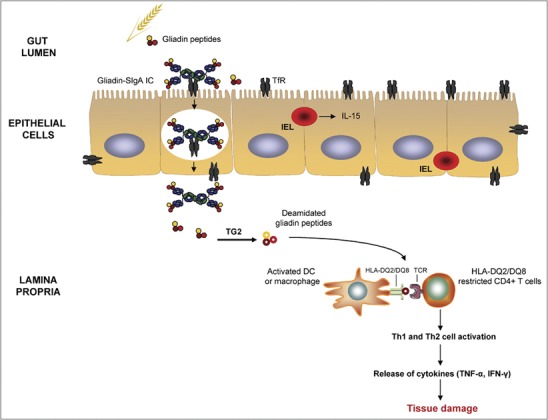
Role of IgA in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. Intact SIgA–gliadin peptide complexes are retrotranscytosed across the lamina propria via TfR, which is abnormally expressed on the apical pole of epithelial cells. Tissue TG2 selectively deamidates gliadin peptides, which bind with high affinity to HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 molecules of antigen-presenting cells. These cells present deamidated gliadin peptides to HLA-DQ2- or HLA-DQ8-restricted populations of CD4+ T cells that become activated and release inflammatory mediators that lead to tissue damage. IL-15, produced by IELs, also participates in the activation of cytotoxicity against enterocytes. IC, immune complex; IEL, intraepithelial lymphocyte; IFN, interferon; IgA, immunoglobulin A; IL, interleukin; SIgA, secretory IgA; TfR, transferrin receptor; TG2, transglutaminase 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
