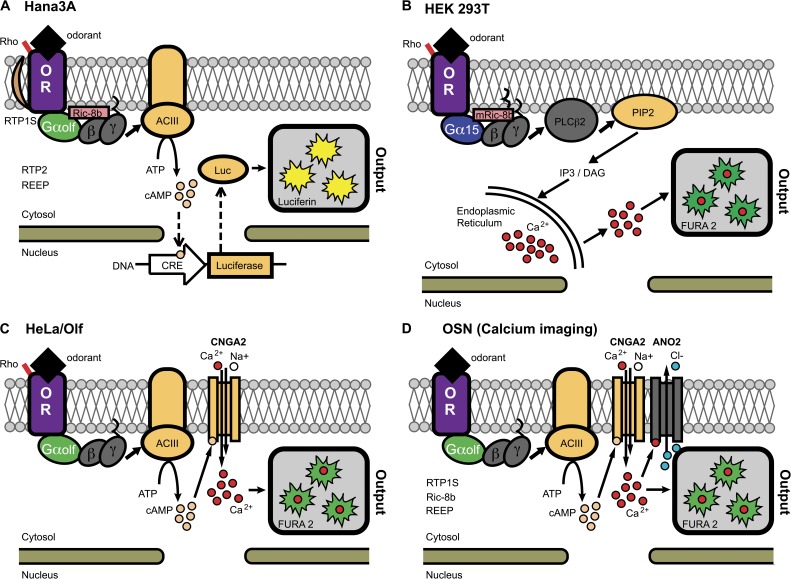
Figure 1.
OR signal transduction and functional readout of the main in vitro assay systems (A–C) and ex vivo dissociated OSNs (D). Salient differences between these assays include the use of N-terminal amino acid tags (e.g., Rho) and trafficking proteins (e.g., RTP1S) to promote cell surface expression, Gαolf or Gα15 G proteins that trigger calcium ion (Ca2+) flux or cAMP production upon ligand binding, and Ric8b or myristoylated Ric8B (mRic8b) proteins that attenuate G protein signaling. RTP2 and REEP are present in Hana3A cells but appear to only marginally improve functional OR expression. RTP1S, REEP, and Ric8b mRNAs are expressed in OSNs, but there is a paucity of evidence for their function there. ACIII, adenylyl cylcase type III; ANO2, anoctamin 2 calcium-activated chloride channel; CNGA2, cyclic nucleotide–gated ion channel A2; CRE, cAMP response element; Luc, luciferase protein; OR, odorant receptor.