Figure 1.
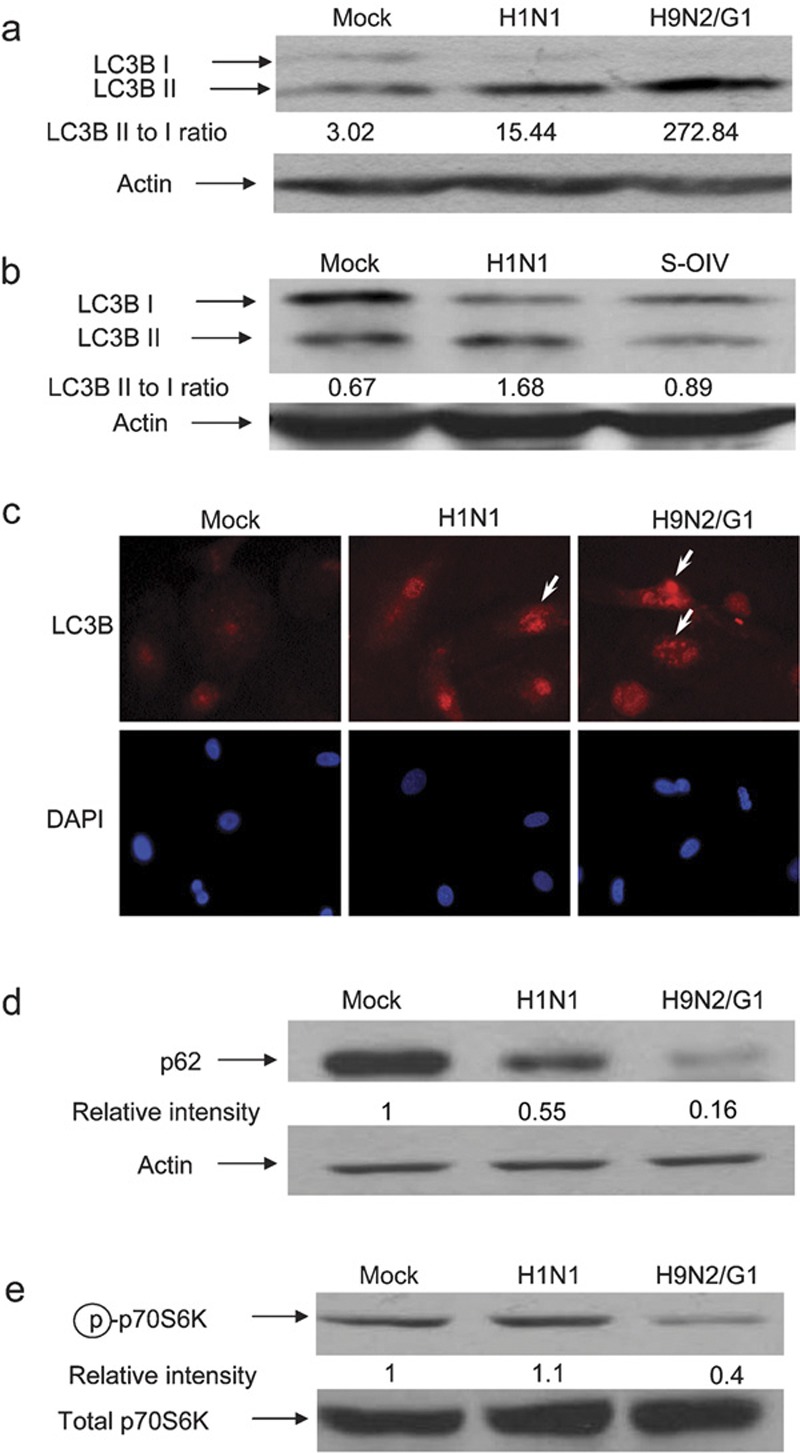
Autophagy was induced by H1N1, H9N2/G1 and S-OIV influenza viruses. Human blood macrophages were mock-infected or infected with H1N1, H9N2/G1 or S-OIV. (a, b) Whole-cell lysates were harvested and LC3B expression was examined by western blot analysis. Actin was used as a loading control. (c) Autophagosomes were examined by staining the mock-, H1N1- or H9N2/G1-infected cells with antibodies specific to LC3B. DAPI was used to stain nuclei. Arrows indicate LC3B positive vesicles. Magnification: ×400. (d) p62 expression levels were examined at 19 h.p.i. by western blot analysis. (e) At 2 h.p.i., phosphorylation levels of p70S6K (Thr389) were examined by western blot analysis. Total p70S6K was used as a loading control. Densities of the protein bands were determined with Bio-Rad Quantity One imaging software. The values in parentheses represent LC3B II to LC3B I ratios (a, b). The p62 (d) and phospho-p70S6K (Thr389) (e) intensity values were normalized to the corresponding actin or total p70S6K values. The values in parentheses are the relative normalized intensities compared to those of the mock-treated cells. The results shown are representative figures from three independent experiments. DAPI, 4,6-diamidine-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride; h.p.i., hour post-infection; p70S6K, p70S6 kinase; S-OIV, swine-origin influenza A/H1N1 virus; Thr389, threonine 389.
