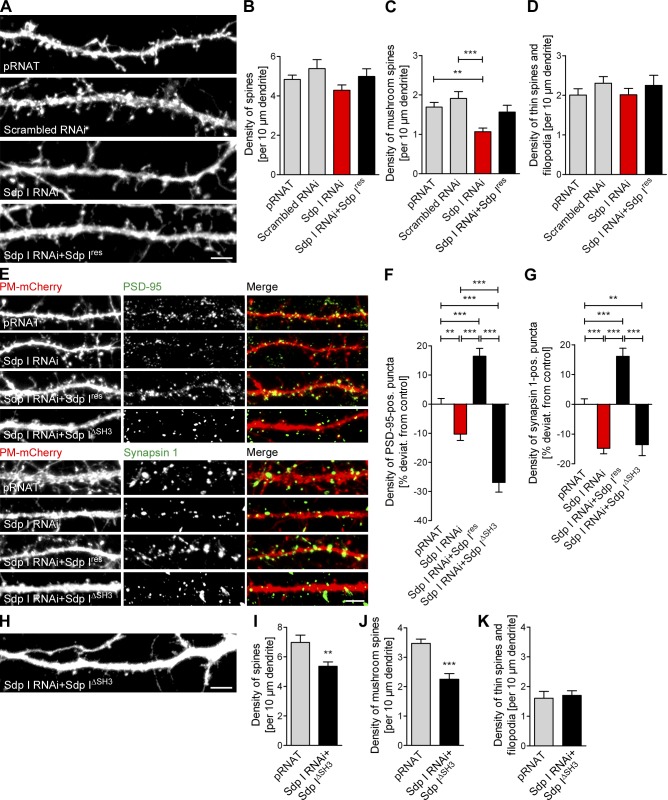
Figure 2.
Impaired spine and synapse formation upon syndapin I loss-of-function is caused by a loss of SH3 domain-dependent syndapin I functions in the postsynaptic compartment. (A and H) PM-mCherry signals of dendrites of neurons transfected as indicated at DIV 12 and fixed at DIV 14. Bars, 5 µm. (B–D) Quantitative analyses of general spine density (B) and of individual morphology groups (C and D) upon syndapin I RNAi. (E) Anti–PSD-95 (postsynaptic) and anti–synapsin 1 (presynaptic) immunolabeling along dendrites of transfected neurons. Bar, 5 µm. (F and G) Quantitation of PSD-95– (F) and synapsin 1–positive puncta (G) spatially overlapping with transfected neurons. (I–K) Quantitative analyses of general spine density (I) and of individual morphology groups (J and K) of syndapin I–depleted cells expressing Sdp IΔSH3 compared with pRNAT control cells transfected in parallel. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Data represent mean ± SEM (error bars).