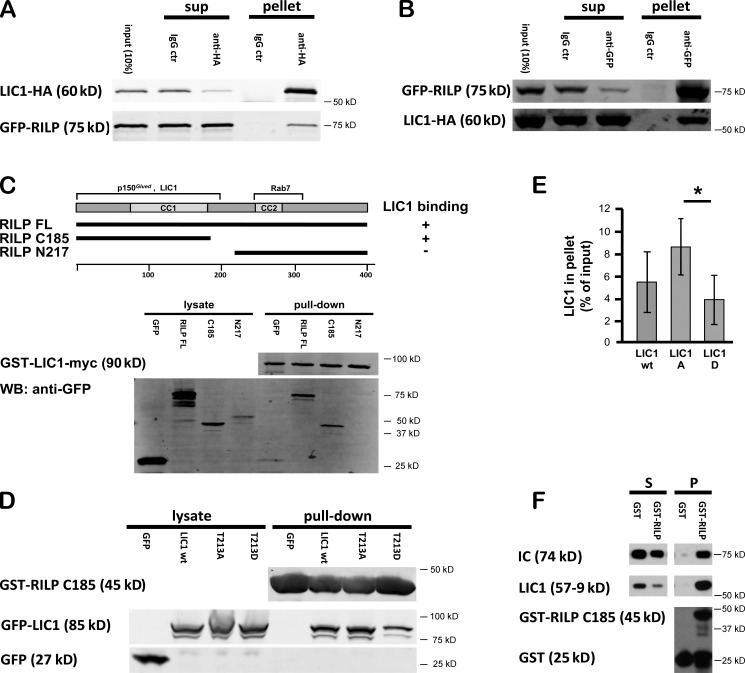
Figure 6.
Interaction of dynein with RILP. (A) LIC1-HA was coexpressed with GFP-RILP and tested for coimmunoprecipitation with an anti-HA mAb. GFP-RILP coimmunoprecipitated with LIC1. ctr, control; sup, supernatant. (B) Reciprocal experiment showing LIC1-HA coimmunoprecipitation with GFP-RILP using an anti-GFP antibody. (C) Mapping of LIC1 interaction site in RILP by GST-LIC1 pull-down of 293A cell-expressed GFP-RILP full-length (FL), 1–185, and 217–401 (C33). Diagram shows RILP constructs and summarizes binding regions for Rab7, dynactin, and dynein. WB, Western blot. (D) GST-RILP 1–185 pull-down experiments using a 293A cell lysate expressing GFP or LIC1 wild type (wt), LIC1-T213A, and LIC1-T213D. Lysate and pellet samples were evaluated for pull-down of LIC1 by immunoblotting with antibodies against GFP. (E) Quantification of data in D. Mean of three independent experiments; error bars represent SDs. RILP 1–185 pulls down more LIC1-T213A than LIC1 wild type or LIC1-T213D. *, P < 0.05. (F) GST-RILP 1–185 pull-down experiments using purified rat brain dynein. Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) samples were evaluated for pull-down of the dynein complex by immunoblotting with antibodies against IC, LIC1, and GST.