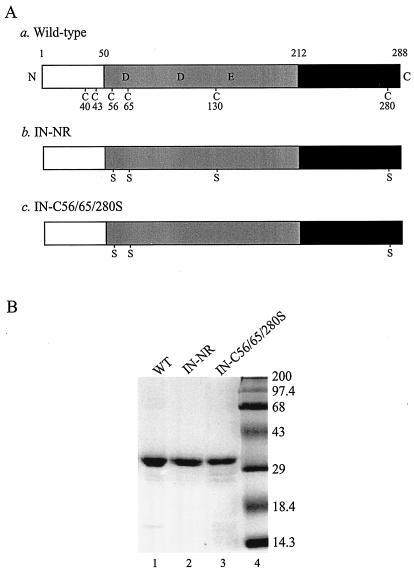
FIG. 1.
Recombinant wild-type and mutant HIV-1 INs. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type HIV-1 IN and Cys mutants used in the in vitro assays. N and C, N and C termini of the protein, respectively. The open boxes represent the N-terminal domain (amino acids 1 to 50) containing the conserved zinc-binding HHCC motif, the shaded boxes represent the central core domain (amino acids 51 to 212) containing the catalytic DD(35)E motif, and the solid boxes represent the C-terminal domain (amino acids 213 to 288). The six Cys residues and their amino acid positions are indicated in the wild-type IN (construct a). Replacements of Cys by Ser are indicated in both IN-NR (construct b) and IN-C56/65/280S (construct c). (B) Coomassie blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of 100 pmol of purified recombinant wild-type IN (WT; lane 1) and its mutant derivatives containing Cys-to-Ser substitutions at positions 56, 65, 130, and 280 (IN-NR; lane 2) or at positions 56, 65, and 280 (IN-C56/65/280S; lane 3). Molecular mass markers (Gibco) are shown in lane 4 and are labeled in kilodaltons on the right.