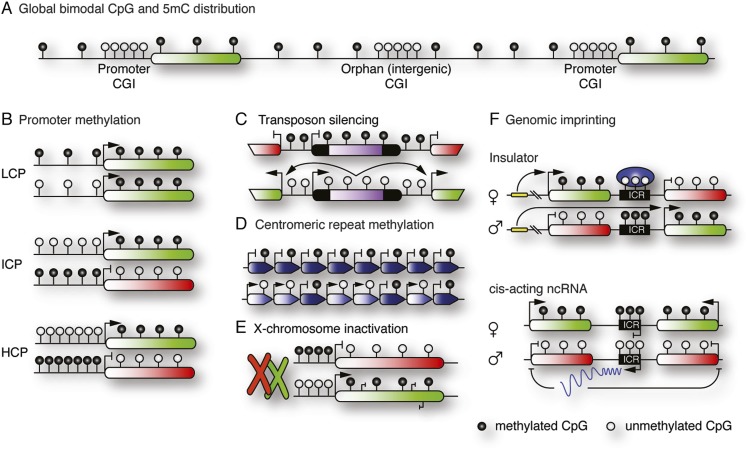
Figure 1.
DNA methylation in the mammalian genome. (A) Genomic CpG distribution: CGIs are generally hypomethylated and found at promoters or intergenic regions (orphan CpG). Non-CGI CpGs are generally hypermethylated. (B) Three categories of gene promoters according to CpG density respond differently to methylation. (LCP) Low CpG density promoter; (ICP) intermediate CpG density promoter; (HCP) high CpG density promoter. (C) Retrotransposons are repressed by DNA methylation. Derepression can result in coactivation of neighboring genes. (D) Basal transcription of centromeric repeats interferes with chromosome alignment and is repressed by DNA methylation. (E) DNA methylation reinforces gene silencing on the inactivated X chromosome. Transcribed genes on the active X chromosome (and globally) display gene body methylation, possibly repressing spurious expression from cryptic transcription start sites or aiding RNA processing. (F) Genomic imprinting drives allele-specific gene expression. DNA methylation at imprinting control regions (ICRs) regulates binding of insulator proteins or expression of cis-acting, noncoding RNAs.