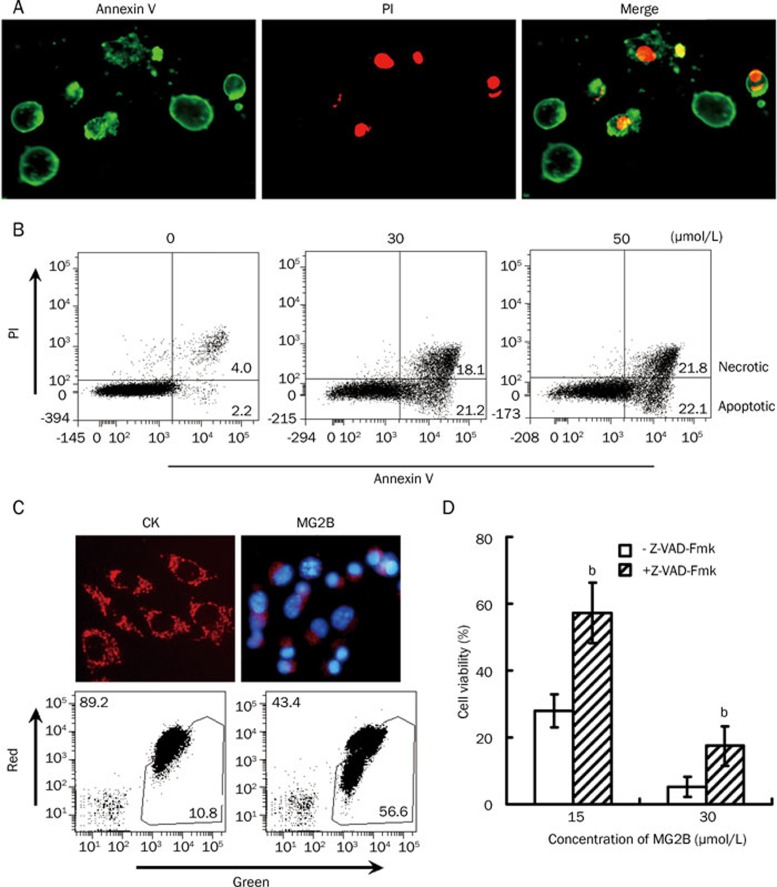
Figure 4.
MG2B induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in tumor cells. (A) Microscope view of MG2B-induced apoptotic cells. After treatment with MG2B, the cells were double stained with FITC-Annexin V (Green) and PI (Red) and then observed under a fluorescence microscope. Annexin V+/PI− cells were considered apoptotic cells at early stages of apoptosis. Annexin V+/PI+ cells were considered apoptotic cells at an advanced stage of apoptosis or necrotic cells. (B) FACS analysis for MG2B-induced apoptotic cells. About 1×105 cells were pooled and incubated with 0, 30, and 50 μmol/L MG2B at 37 °C for 1 h. Peptide-treated cells were then double stained with FITC-Annexin V and PI and assayed by FACS. The percentage of apoptotic (Annexin V+/PI−) and necrotic (Annexin V+/PI+) cells is indicated. (C) MG2B-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane potential in MCF-7 cells. To observe the mitochondria in cells, the adherent MCF-7 cells (1×104 cells/well) were incubated with 100 μL MG2B (20 μmol/L) at 37 °C for 2 h followed by staining with JC-1 and observed under a fluorescence microscope. To analyze the mitochondrial membrane potential by FACS, 1×105cells were collected and incubated with 100 μL MG2B (0, 75 μmol/L) at 37 °C for 1 h followed by staining with JC-1 and washing with PBS. The percentage of red and green cells is indicated. (D) Inhibition of the MG2B-induced cell death by pan-caspase inhibitor. Cells (1×104cells/well) were preincubated with 100 μmol/L of pan-caspase inhibitor z-VAD-Fmk for 2 h at 37 °C before addition of peptide. The cytotoxicity of MG2B (15–30 μmol/L) in MCF-7 cells was then determined using the CCK-8 reagent. The cytotoxicity of MG2B in MCF7 cells in the presence of z-VAD-Fmk is significantly (bP<0.05) different from the cytotoxicity of MG2B in the absence of z-VAD-Fmk.