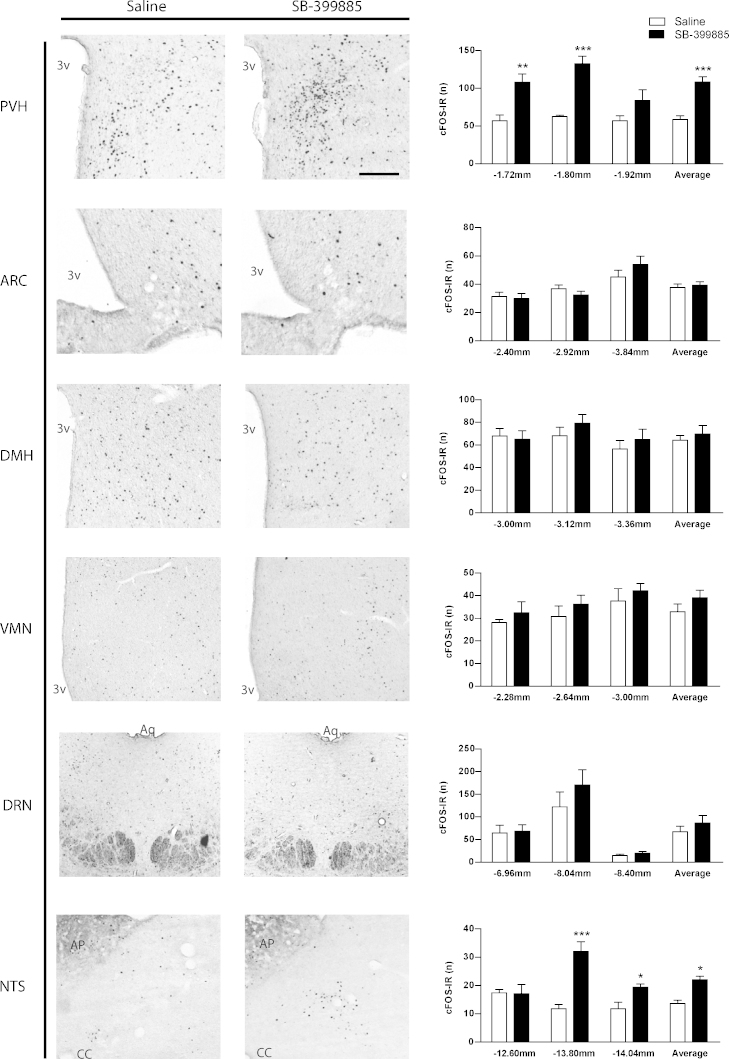
Fig. 3.
SB-399885 significantly increased FOS-IR in the PVH and NTS compared to saline. Counts of FOS-IR (n) in the PVH, ARC, DMH, VMN, DRN, and NTS following treatment with saline (white bar) or 2 mg/kg SB-399885, and accompanying representative photomicrographs. SB-399885 significantly increased FOS-IR in the PVH at −1.72 mm (t10 = 3.77, p = 0.01) and −1.80 mm (t test, t10 = 7.06, p < 0.0001) from bregma, and at the level of the area postrema in the NTS at −13.80 mm (t10 = 5.45, p = 0.001) and −14.04 mm (t test, t10 = 3.1, p = 0.01). Scale bar = 50 μm. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M., *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 compared to saline treatment. Abbreviations: PVH, paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; ARC, arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus; DMH, dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus; VMN, ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus; DRN, dorsal raphe nucleus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; cc, central canal; Aq, aqueduct and AP, area postrema.