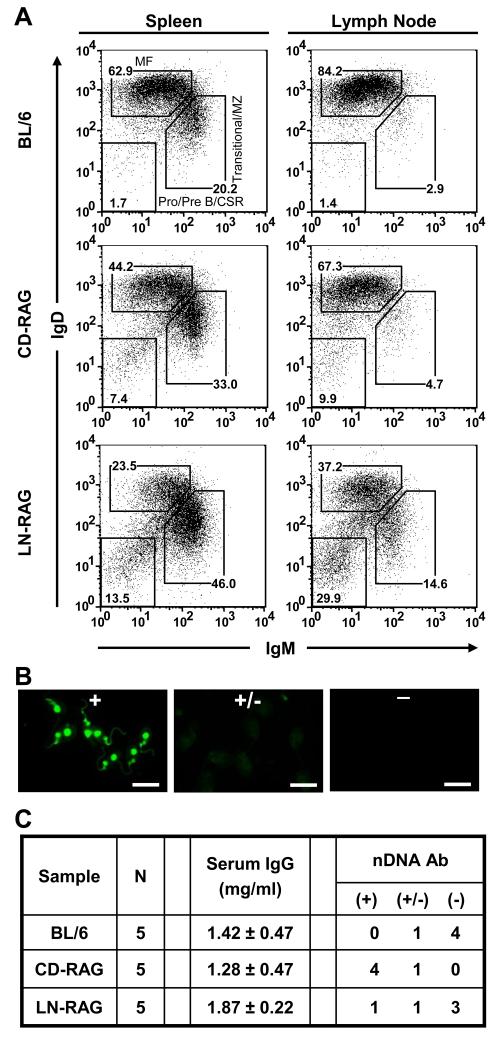
Figure 5. RAG-1−/− mice reconstituted with CD B cells, but not LN B cells, results in serum autoantibody.
Non-adherent BL/6 BM cells were cultured to generate CD B cells for injection into B6.RAG-1−/− mice as previously described (37). BL/6 LN cells were isolated for transfer into B6.RAG-1−/− mice (LN-RAG). (A) At 6 wk post-transfer, spleen and LN cells from BL/6 (top), CD-RAG (middle) or LN-RAG (bottom) mice were labeled with mAbs to B220, IgM, and IgD. Flow diagrams were pre-gated on live, single, B220+ cells and B220+ cells were subdivided into IgM−IgD− pro-/pre-B/CSR B, IgMhiIgDlo transitional/MZ B, and IgMintIgDhi MF B cell compartments. Data are representative of each mouse analyzed (n=5 per group). Sera from each experimental group were collected via retro-orbital eye bleeding at 6 wk post-transfer. (B) Sera samples were diluted (1:160) and used to labeled C. luciliae substrate slides. After overnight washing, Ab bound to cells was detected using rat anti-mouse IgG-FITC Ab. All images were acquired using a Zeiss Axiovert 200M confocal immunofluorescent microscope with an exposure time of 300ms at 400x magnification. Representative examples of strong (++), weak (+) and no (−) nDNA binding activity are presented. Scale bar equals 20μm for all images. (C) Concentrations of serum IgG were determined using anti-mouse IgG-specific ELISAs including standard curves. Each sera sample (1:160 dil) was screened for reactivity to nDNA by immunofluorescent microscopy with a fixed exposure time (300ms) at 400x magnification. Each group contained multiple mice (n=5) that were screened independently.