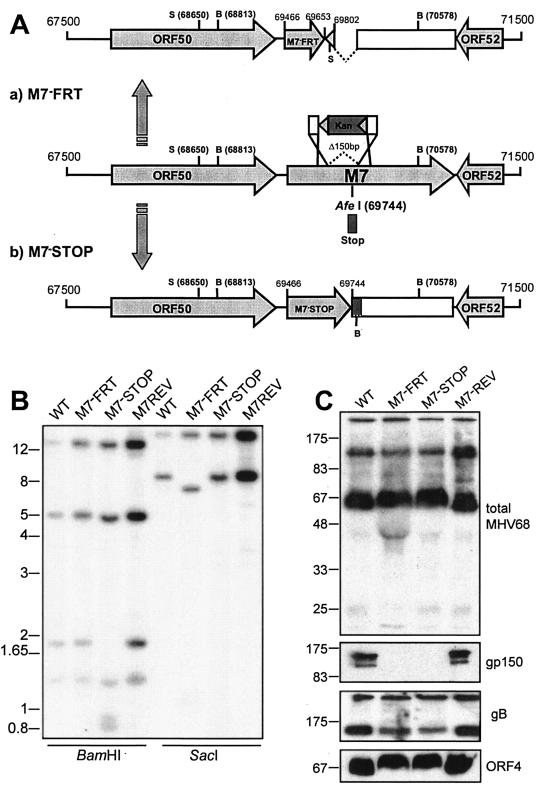
FIG. 1.
Mutagenesis of the MHV-68 M7 gene encoding gp150. (A) The M7−FRT mutant was made using RecE/T to insert an FRT-flanked kanamycin resistance (Kan) gene in place of genomic coordinates 69653 to 69802. The resistance gene was then removed with Flp recombinase, leaving a single FRT site plus short flanking plasmid sequence, including a SacI restriction site. This mutant was reverted by RecA-mediated replacement of the M7 locus with an unmutated BglII genomic clone (67744 to 73044). The M7−STOP mutant was made by inserting an oligonucleotide containing multiple stop codons in all three frames into an AfeI site (genomic coordinate 69744) of the BglII clone. The oligonucleotide also included a BamHI restriction site. The mutated BglII clone was then recombined into the WT MHV-68 BAC using RecA. SacI (S) and BamHI (B) restriction sites are indicated. (B) Southern blots of viral DNA, digested with BamHI or SacI and probed with a SacI genomic fragment (68650 to 76030). BamHI digestion of M7−STOP cut the WT 1,765-bp band into 931- and 834-bp fragments; SacI digestion of M7−FRT cut the WT 7,380-bp band into 6,370- and 1,010-bp fragments. (C) Immunoblot analysis of gp150-deficient viruses. Titers of GFP+ virus stocks were determined by infecting BHK-21 cells with serial fivefold virus dilutions. The proportion of BHK-21 cells expressing GFP after 16 h was determined by flow cytometry. There was no significant difference between the GFP titer and the plaque titer for either M7− or M7+ viruses. Unreduced lysates equivalent to 105 GFP+ infectious units were then separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotted for virion components, using either a rabbit serum raised against whole virus (total MHV-68) or MAbs specific for gp150, gB, and ORF4, as indicated.