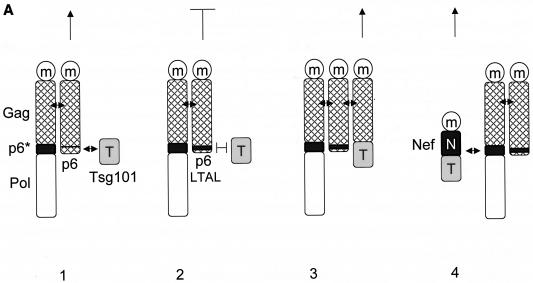
FIG. 5.
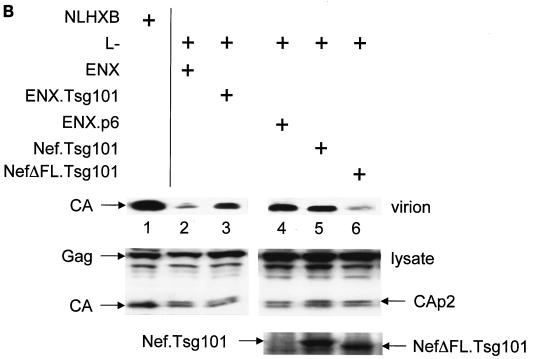
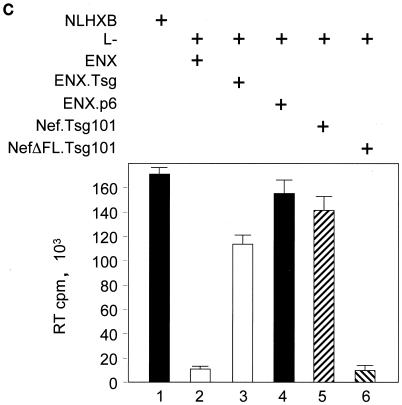
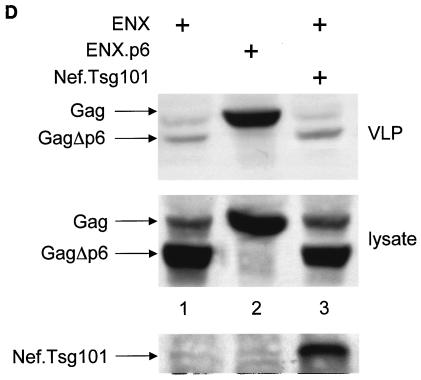
The Nef.Tsg101 chimera but not the mutant NefΔFL.Tsg101 chimera rescues mutant HIV-1 in the PTAP motif of the late domain. (A) Schematic representation of the trans-complementation assay for virus release. By recruiting Tsg101 to the PTAP domain of viral protein p6, cells expressing the HIV-1NLHXB provirus are able to release new virions to the supernatant (panel 1). To create the L− proviral clone, the two prolines in the PTAP motif in p6 of HIV-1NLHXB were mutated to leucines (PTAP→LTAL). Cells expressing the L− provirus no longer release virions to the supernatant (panel 2). To rescue this release, this L− mutant provirus was coexpressed with compensatory late domains (added back to a HIV-1NLHXB mutant, named ENX, with p6, pol, vif, vpr, and nef deleted) in 293T cells (panel 3). In another scenario, the L− provirus was coexpressed with a plasmid expressing the Nef.Tsg101 chimera (panel 4). (B) Cellular supernatants were harvested, and virions were precipitated by ultracentrifugation. Western blotting of virion preparations and cell lysates were performed with the anti-CA antibody. Lysates were also analyzed by Western blotting with the anti-Nef antibody for the presence of the Nef.Tsg101 chimera. Arrows indicate the Gag (55 kDa) and MACA (41 kDa) precursors, the CA (24 kDa) protein, and the Nef.Tsg101 (∼83 kDa) and the NefΔFL.Tsg101 (∼80 kDa) chimeras. (C) An aliquot of each virion preparation was used to determine amounts of virus present in supernatants of transfected cells (RT). The wild-type HIV-1NLHXB (bar 1) and the L− proviruses plus ENX.p6 (bar 4) were used as positive controls for virion production. The L− provirus plus the plasmid ENX were used as negative control for the trans-complementation assay (bar 2). The mutant NefΔFL.Tsg101 fusion protein (bar 6) was used as the negative control for the binding between HIVNef and GagPol (bar 5). (D) The Nef.Tsg101 chimera does not rescue the release of VLPs from ENX. VLPs from supernatants of cells expressing ENX, expressing ENX.p6 as a positive control, or coexpressing ENX with the Nef.Tsg101 chimera were collected and purified. Viral and cell-associated proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with the anti-CA antibody. Arrows indicate the Gag (55 kDa) and mutant GagΔp6 (49 kDa) proteins. The presence of the Nef.Tsg101 chimera was also confirmed.