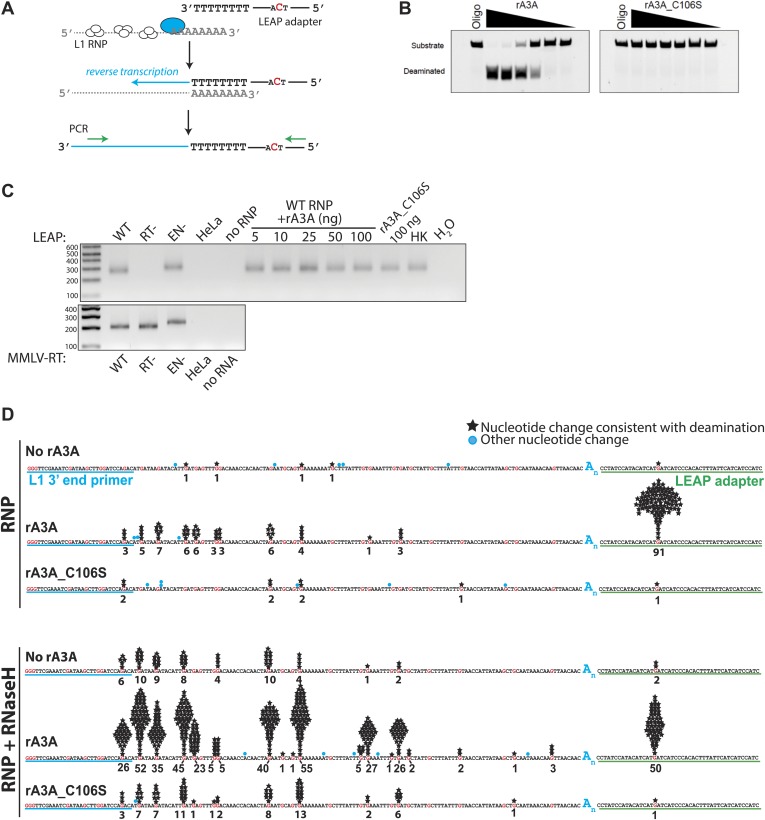
Figure 2. Recombinant A3A (rA3A) deaminates L1 cDNAs in vitro.
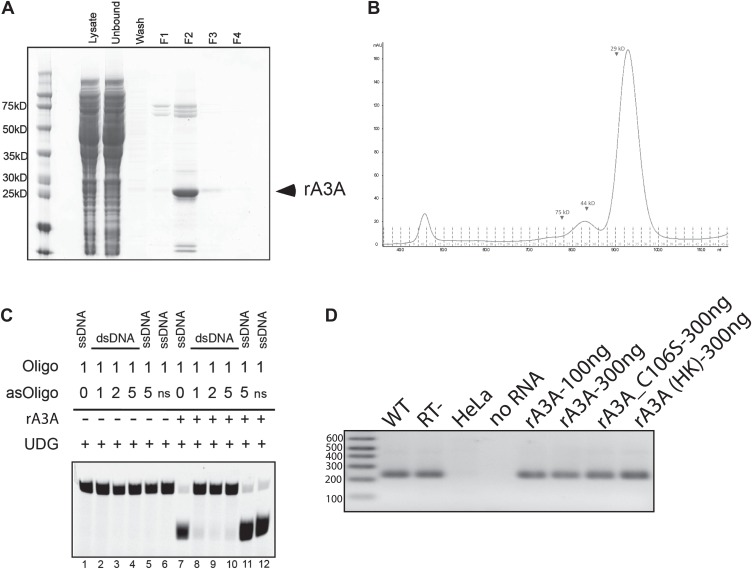
(A) LEAP assay rationale: L1 RNP preparations consisting of the L1 RNA (gray), L1 ORF1p (white ovals), and L1 ORF2p (blue oval) are incubated with a 3′ RACE primer consisting of a unique adapter sequence that contains a single cytidine (red) followed by an oligo dT sequence (black lettering). After reverse transcription (blue arrow), the resultant L1 cDNAs (blue line) are PCR amplified using primers specific to the engineered L1 and the unique adapter sequence (green arrows). (B) Recombinant A3A has deaminase activity in vitro: twofold serial dilutions (500 ng–15.62 ng) of WT rA3A (left panel) or deaminase-deficient rA3A_C106S (right panel) were incubated with a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) labeled single-strand DNA oligonucleotide containing a single cytidine residue. The products were treated with recombinant uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) and NaOH and then were resolved by gel electrophoresis. A control reaction was included without recombinant protein (marked Oligo). (C) Recombinant A3A does not inhibit L1 RT activity: control LEAP reactions with RNP preparations from HeLa cells transfected with WT (pDK101), RT- (pDK135), or EN- (pJJH230A/L1.3) human L1s (upper gel). HeLa indicates untransfected HeLa cells; no RNP indicates control reactions lacking RNPs. Increasing amounts of rA3A (ng) did not significantly affect LEAP activity. Samples containing a deaminase-deficient rA3A_C106S, a heat killed rA3A (HK), or without LEAP products (H2O) served as controls. MMLV RT reactions (lower gel) confirm the integrity of purified RNA isolated from RNP preps used in the LEAP assay. Notably, the increased size of the EN- RNP RT products is due to a higher molecular weight product generated from pJJH230A/L1.3, which contains an mblastI indicator cassette instead of an mneoI indicator cassette. Size standards (bp) are indicated at the left of the gel. (D) Sequence characterization of LEAP Products: shown is the (+) strand sequence of the LEAP product. Guanosine nucleotides are indicated in red. Black stars and numbers indicate the frequency of G-to-A mutations (corresponding to C-to-U mutations in the minus (−) strand L1 cDNA) that occurred on (+) strand L1 cDNA. Blue circles indicate other nucleotide changes. The blue An indicates the LEAP product poly (A) tail. Blue underlining indicates the L1 3′ end PCR primer. Green underlining indicates the LEAP adapter (5np1) sequence. Top panel: LEAP products generated under the following conditions: no rA3A protein, 100 ng of wild-type rA3A, 100 ng of deaminase-deficient rA3A_C106S. Bottom panel: LEAP products generated under the following conditions in the presence of RNase H: no rA3A protein, 100 ng of wild-type rA3A, 100 ng of deaminase-deficient rA3A_C106S. One hundred products were characterized for each condition.