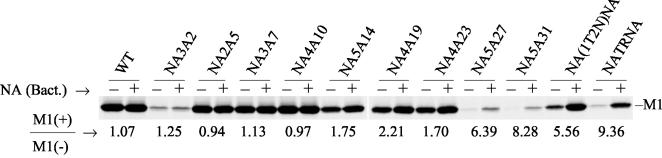
FIG. 5.
Effect of bacterial NA on virus release. Virus-infected MDCK cells were metabolically labeled (at 5 h p.i.) with 300 μCi of 35S-protein labeling mix in 2:8 VGM for 9 h. Two hours before collection, virus-infected cells were treated (+) or mock treated (−) with bacterial NA (10 mU/ml). At 14 h p.i., released virus particles in the supernatant were collected and clarified by low-speed centrifugation and virions were purified and pelleted by ultracentrifugation through a 25% sucrose cushion. Pellets were dissolved in TNE buffer. Viral proteins were analyzed directly by SDS-PAGE, autoradiographed, and quantified. The increase in virus release after NA treatment was determined by using the M1 band. The average value of M1(+)/M1(−) was calculated from the results from three to five independent experiments, with a variation of less than 10%.