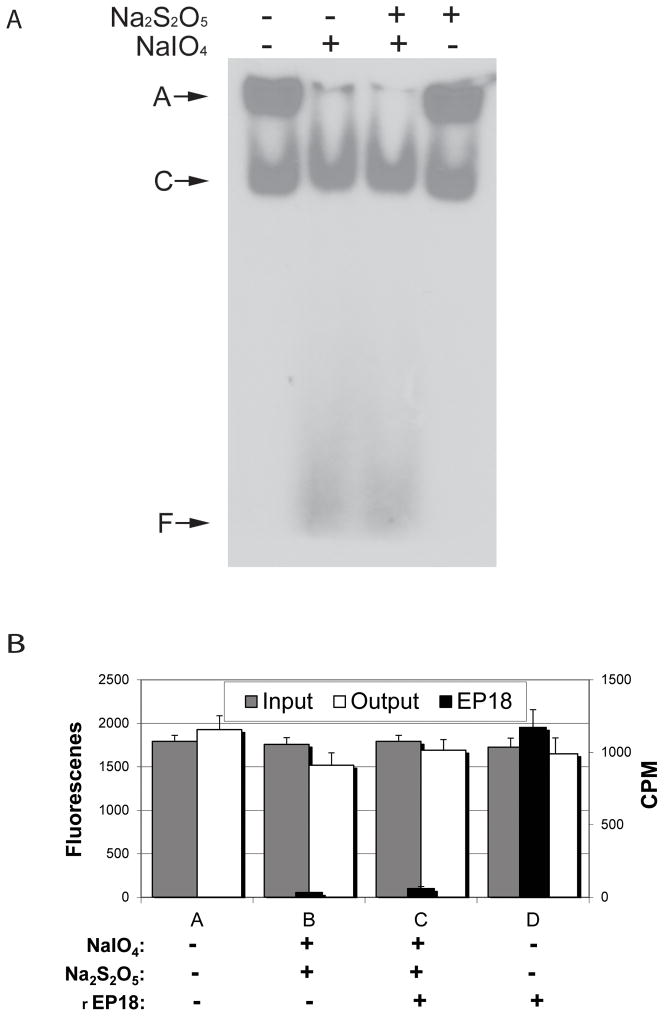
Figure 7. The chemical reactions do not affect the gel shift assay for nuclear extract C/EBP, and when mixed, rEP18 couples but GFP-C/EBP does not.
A, 5 μl 20 nM radiolabeled EP18 in buffer KP is mixed with 5 μl 5 mg/ml HEK 293 nuclear extract, and 1 μl 100 mM NaIO4 (or water) is added, the mixture is incubated in the dark for 1 h at 20°C, and then 1 μl 200 mM Na2S2O5 (or water) is added, and further incubated for 30 min. The samples were then mixed with 5 μl BPB-Glyc and 15 μl buffer GS, and 20 μl was loaded on a 5% native PAGE for a gel shift assay. After electrophoresis, the gel was dried and exposed to film for autoradiography. A, an aggregate which didn’t enter the gel; C, the shifted DNA-protein complex; F, free DNA. B, GFP-C/EBP (30 μM) in buffer KP was either mixed with buffer or radiolabeled rEP18 in buffer to give a final concentration of 20 nM DNA as indicated in the figure. The mixture was divided into portions and either reacted with water or NaIO4 and NaS2O5 as indicated at a final concentration of 1 mM each. Portions of each reaction were saved (to determine input, gray bars) or mixed with 10 μl of hydrazide-agarose and allowed to couple for 2 h at 20°C. After coupling, the resin was washed 3 times with 10 volumes of TE1.0 buffer. The washes were combined and either scintillation counted (Cerenkov radiation, CPM, black bars) or the fluorescence was determined (output, white bars) as indicated. All determinations are in triplicate and error bars show standard deviation. The only statistical difference between these data are reacted rEP18 (C) versus unreacted (D, p<0.05).