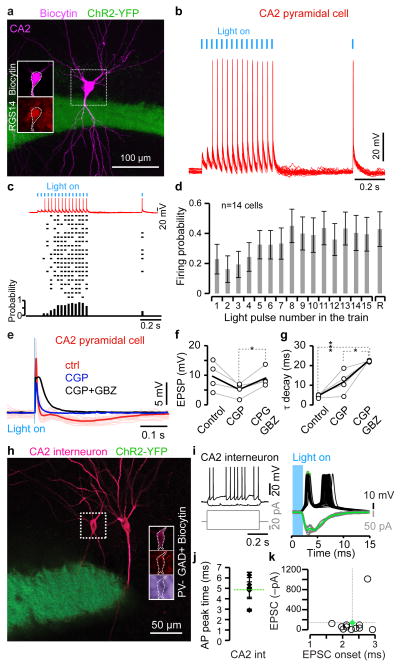
Figure 5. Response of CA2 cells to optogenetic stimulation of mossy fibers (MFs).
a, Z-projected confocal image of biocytin-filled CA2 pyramidal cell. Note ChR2-YFP-positive MFs. Inset from the dotted-line box: single confocal stacks showing biocytin (top) and RGS14 staining (bottom). b, Patch-clamp recording from a CA2 pyramidal cell (same as a) in current mode showing the spiking activity in response to optogenetic stimulation (30 Hz train) of MFs. c, Spiking activity of the same CA2 cell. Bottom: firing probability. d, Average firing probability in response to a 30 Hz train of light pulses for n=14 CA2 pyramidal cells. Note the increased probability in the recovery pulse R. e, Current clamp recording from a CA2 pyramidal cell in response to optogenetic stimulation of MFs showing a large EPSP (average of 30 traces in red) followed by inhibition sensitive to antagonists of GABAergic transmission (blue CPG, black GBZ). f–g, EPSP amplitude and decay, as shown in (e), are affected by GABAa and GABAb antagonists (two-tailed paired t-test: ***P<0.001, *P<0.05, n=4). Average: black lines. h, Z-projected confocal image of a biocytin-filled (violet) CA2 interneuron. Inset from the dotted line-box: CA2 interneuron GAD67-positive and parvalbumin-negative. Note the ChR2-YFP-positive MFs in green. i, Current (black) and voltage clamp recordings (green) of the same CA2 interneuron in (h), in response to optogenetic stimulation of MFs. Note the spiking activity (action potential peak time: green asterisks). Inset: intrinsic electrophysiological properties in response to current steps. j, First action potential peak times from n=5 CA2 interneurons in response to optogenetic stimulation of MFs (average: green dotted-line). k, EPSC amplitudes and onsets from n=11 CA2 interneurons in response to optogenetic stimulation of MFs (average: green dot).