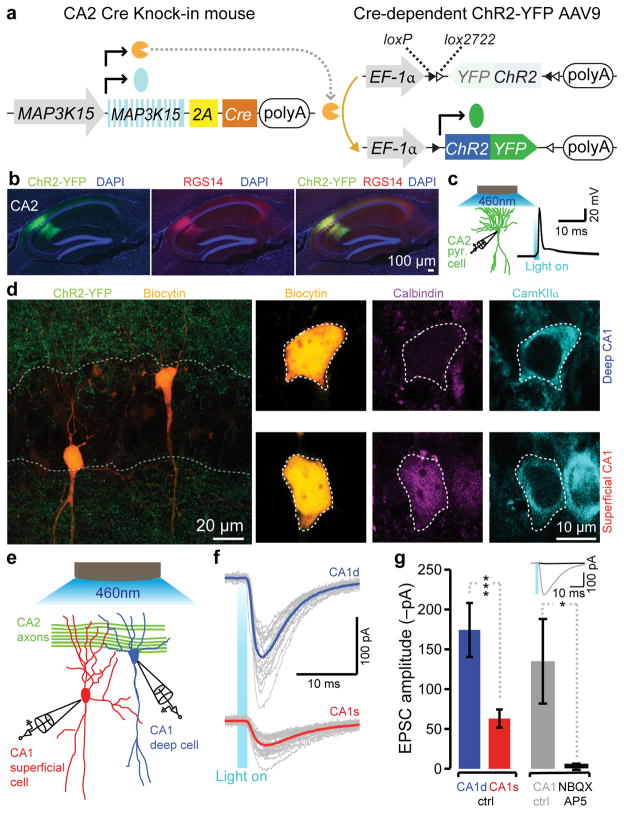
Figure 8. A preferential connection from CA2 to deep CA1 pyramidal cells establishes a novel trisynaptic circuit: DG-CA2-CA1deep.
a, CA2-specific Cre knock-in mice were injected with Cre-dependent AAV9-EF1α-ChR2-YFP. Cre-recombinase switches on the expression of ChR2-YFP in CA2. b, ChR2-YFP expression in RGS14-positive CA2 cells. c, Optogenetic stimulation of a ChR2-YFP-positive CA2 pyramidal cell. d, Representative image of a recorded CA1 pyramidal cell pair located in different sublayers (dotted line: pyramidal cell layer). Upper side-panels: deep cell CaMKIIα-positive and calbindin-negative. Lower side-panels: superficial cell CaMKIIα-positive and calbindin-positive. e, Patch-clamp recordings of CA1 superficial and deep pyramidal cells combined with optogenetic stimulation of CA2 fibers in acute hippocampal slices. f–g, Optogenetic stimulation of CA2 fibers elicited EPSCs in a CA1 pyramidal cell pair. Deep pyramidal cells displayed a stronger response (n=14 pairs, two tailed paired t-test: ***P<0.001). EPSCs were sensitive to NBQX/AP5 (n=7, two tailed paired t-test: *P<0.05). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.