Figure 1.
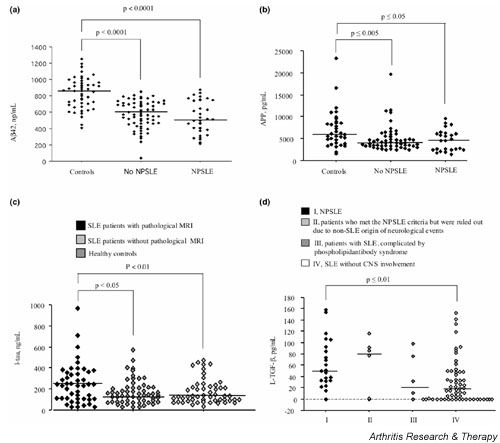
Decreased levels of soluble amyloid β-protein precursor and β-amyloid protein but increases of intrathecal axonal degradation products and TGF-β in patients with cerebral lupus. (a) Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) content of soluble amyloid β-protein (Aβ42) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) with and without central nervous system (CNS) engagement, as well as in cerebrally healthy control subjects. (b) CSF content of amyloid precursor protein (APP) in patients with SLE with and without CNS engagement, as well as in cerebrally healthy control subjects. (c) CSF content of tau in patients with SLE stratified with respect to brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-verifiable changes, and in cerebrally healthy control subjects. (d) CSF content of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) in SLE patients stratified with respect to the presence/absence and type of CNS engagement. NPSLE, neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus.
