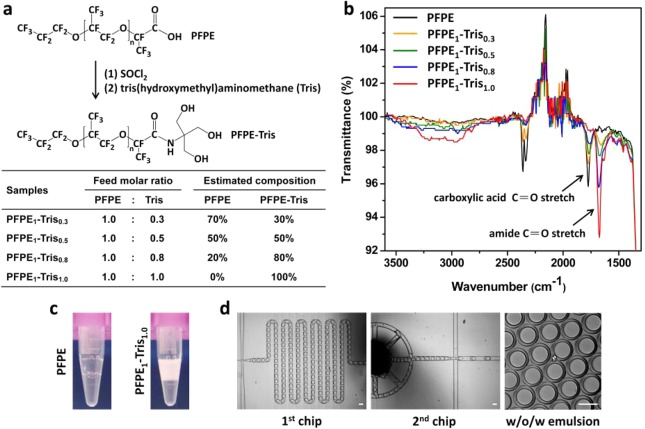
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of PFPE–Tris surfactants with estimated composition and (b) the corresponding FT-IR spectra. The absorbance peak at 1775 cm–1 corresponds to the carboxylic acid C=O stretch of unreacted PFPE, whereas the absorption peak at 1675 cm–1 represents the converted amide C=O stretch. The maximal conversion occurred when the absorbance peak of 1775 cm–1, representing the amount of the unreacted PFPE, completely disappeared, at the feed molar ratio of 1.0. The percentage of conversion, shown as a table in (a), was estimated by the relative peak height on the FT-IR spectra. (c) Photographs of off-chip collected w/o emulsion generated by a flow-focusing droplet generator with 2 wt % unmodified PFPE or PFPE1–Tris1.0 dissolved in HFE-7500 as the oil phase. (d) Formation of water-in-oil-in-water (w/o/w) double emulsion by a two-step emulsification process using two integrated microfluidic chips (scale bar: 100 μm) and 2 wt % PFPE1–Tris1.0 in HFE-7500 as the oil phase.