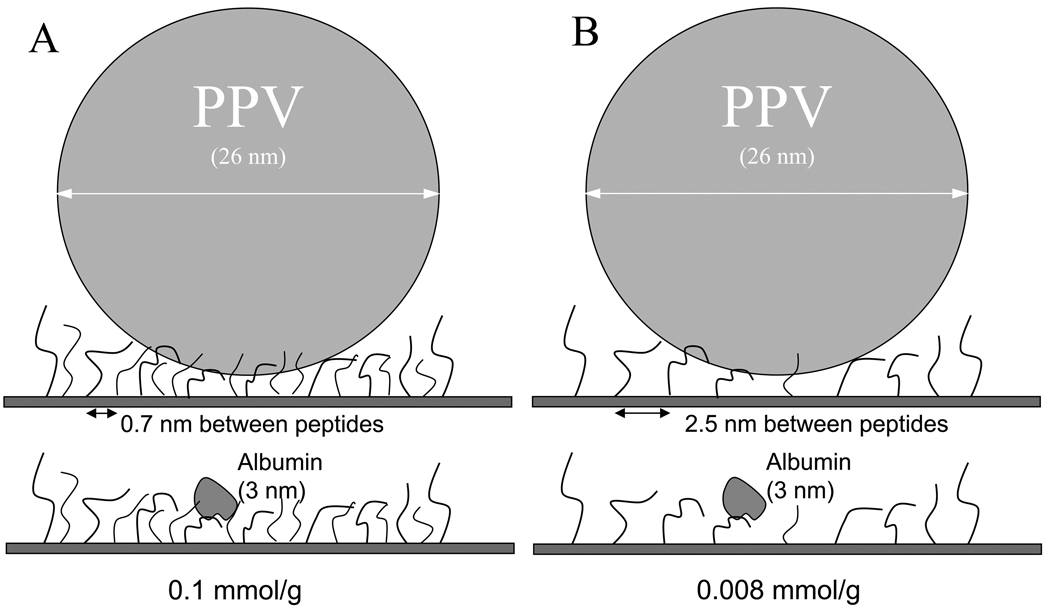
Figure 1.
Hypothesized effect of high versus low density peptides. (A) At a concentration of 0.1 mmol/g, multiple peptides bind to both the virus and competing proteins (e.g., albumin). (B) At a density of 0.008 mmol/g, multiple peptide-virus contact points promotes virus binding, but limited (monomeric) peptide binding to smaller completing proteins reduces the likelihood and strength of non-specific binding, hence improving the performance of the peptides for virus capture.