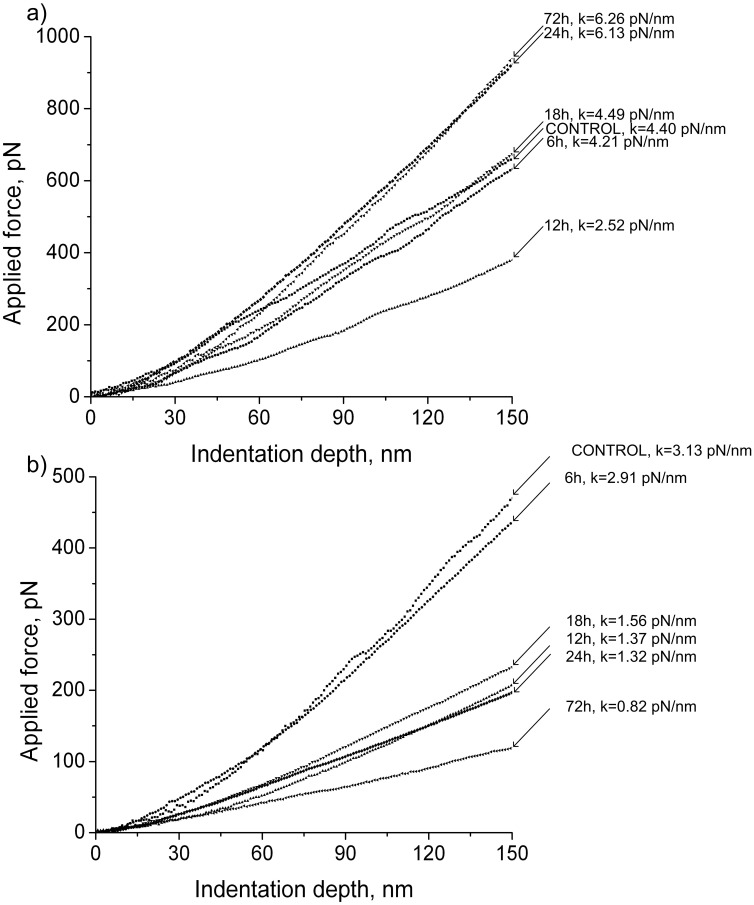
Figure 1. Typical force curves obtained under transversal stiffness measurements of rat left ventricle cardiomyocytes (A) and soleus fibers (B) of the rats under short-term antiorthostatic suspension.
(A) – changes in the transversal stiffness of cardiomyocytes were sharp and in different directions: first, the stiffness was reduced and then restored to control levels and further exceeded it. (B) – the transversal stiffness of soleus muscle fibers was reduced in steps: falling in 12 hours and remaining at this level up to 24 hours of suspension and then dropping back to 72 hours of gravitational unloading.