FIGURE 10:
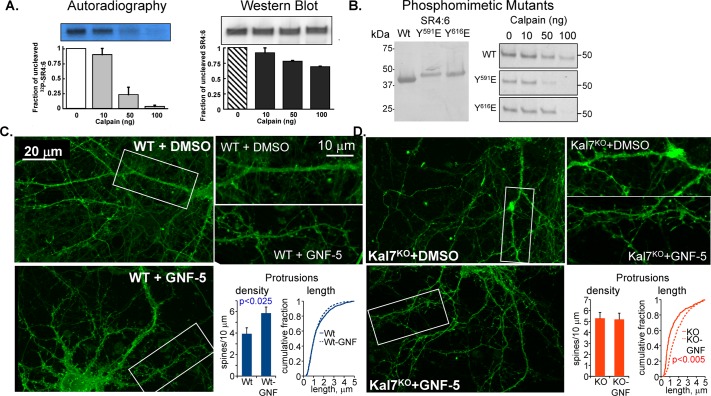
Phosphorylation of KalSR4:6 by Abl1 increases its sensitivity to calpain. (A) KalSR4:6 phosphorylated with [γ-32P]ATP by Abl1 or exposed to the same conditions in the absence of ATP and Abl1 was exposed to the indicated amount of μ-calpain for 60 min at 37°C. Digested samples were fractionated by SDS–PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes; 32P-labeled KalSR4:6 was visualized by autoradiography (left), and unlabeled KalSR4:6 was visualized by Western blot (right) using an antibody to SR4:7 (JH2580; Penzes et al., 2000). The amount of intact KalSR4:6 remaining was quantified; error bars show range of duplicate experiments. (B) Purified recombinant KalSR4:6 and KalSR4:6 with a phosphomimetic mutation at position 591 (SR4:6/Y591E) or 616 (SR4:6/Y616E) was fractionated by SDS–PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and visualized with Coomassie brilliant blue; mutation of either Tyr residue altered the mobility of the protein during electrophoresis. The purified proteins (1 μg each) were exposed to the indicated dose of μ-calpain as described. The reaction was stopped, and the SDS–PAGE fractionated products were visualized with Coomassie; mutation of either site increased the calpain sensitivity of the protein. (C, D) DIV18 cortical neurons from WT (C) and Kal7KO (D) mice were exposed to medium containing 10 μM GNF-5 in DMSO, or an equivalent volume of DMSO, for 6 h and fixed. Images obtained using an Axiovert 200M with Apotome for optical sectioning were coded and scored by a blinded observer. GNF-5 increased the dendritic protrusion density in WT but not Kal7KO neurons (C) while increasing the protrusion length in Kal7KO but not WT neurons (D). N = 9–14 WT neurons and 6–8 Kal7KO neurons; N = 1187–1652 WT protrusions and 306–838 Kal7KO protrusions.