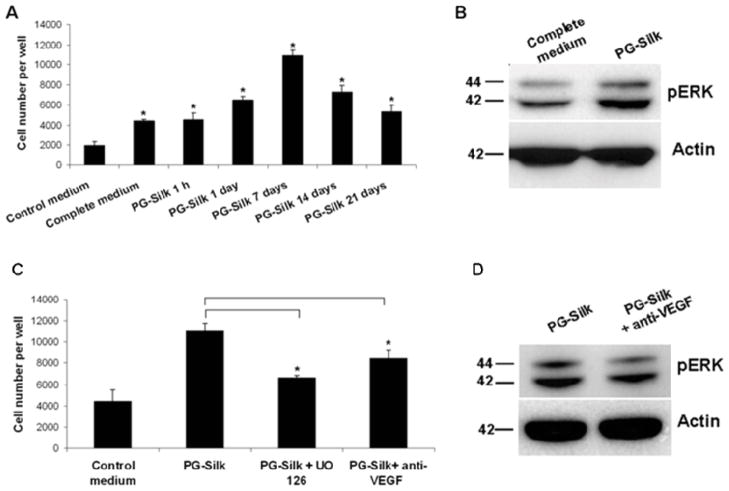
Fig. 2. VEGF and pERK signaling in HUVEC proliferation induced by PG-Silk.
(A) PBS supernatant collected from PG-Silk (25% v/v with control media) was used to inoculate HUVEC cells. The MTS assay was conducted after 3 days. * denotes statistically significant difference compared with the control medium (p < 0.05). (B) Representative immunoblotting image showing a increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation in HUVEC cells cultured with PBS supernatant collected from PG-Silk, as compared to cells cultured with complete media. Actin was used as control of protein equal loading. (C) HUVEC cells were cultured in PBS supernatant collected from PG-Silk (25% v/v with control media) in presence of UO 126 or anti-VEGF neutralizing antibody. The MTS assay was conducted after 3 days (p < 0.05). (D) Representative immunoblotting image showing a decreased ERK1/2 phosphorylation in HUVEC cells cultured 2 hrs with PBS supernatant collected from PG-Silk in presence of anti-VEGF. Actin was used as control of protein equal loading.